Understanding soil pH is like cracking the secret code to a thriving, vibrant garden. With this knowledge, you can ensure your plants receive the nutrients they need to flourish.
This article uncovers 15 essential facts about soil pH to help unlock your garden's full potential. So, strap in, and let's dive into the exciting world of soil chemistry!

1. What is soil pH?
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of your soil. It's determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the soil solution.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH below 7 indicates acidic soil, while a pH above 7 signifies alkaline soil.
2. Why is soil pH important?
Soil pH influences the availability of nutrients in the soil, directly affecting plant health. Some nutrients are more accessible at certain pH levels, while others become less available.
A balanced soil pH ensures plants can effectively absorb the nutrients they need to grow and thrive.
3. How to test soil pH?
To determine your soil's pH, you can use a pH test kit, a soil pH meter, or send a soil sample to a testing laboratory.
Regularly testing your soil pH helps you maintain the optimal conditions for your plants and address any potential issues.
4. Ideal soil pH for different plants
Different plants have different soil pH preferences. For example, blueberries and azaleas thrive in acidic soil, while lilacs and clematis prefer alkaline conditions.
Knowing the ideal pH for each plant species in your garden will help you create a harmonious environment that encourages growth and resilience.
5. Planting zones and soil pH

Soil pH can vary across planting zones due to climate, geography, and soil composition.
Familiarize yourself with the natural pH tendencies in your area to make informed decisions about the plants you choose and how to manage your soil pH.
6. How to lower soil pH (acidify soil)
If your soil is too alkaline, add organic materials like peat moss, compost, or decomposing leaves to lower the pH.
Another option is to apply elemental sulfur, aluminum sulfate, or iron sulfate, which can help acidify the soil more quickly.
7. How to raise soil pH (alkalize soil)

You can apply lime (calcium carbonate) or wood ashes to raise your soil's pH and make it more alkaline.
Remember to follow the recommended application rates and retest your soil pH to avoid overcorrecting the problem.
8. Soil pH and nutrient availability
The availability of essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, is affected by soil pH.
For instance, acidic soil can cause nutrient deficiencies, while alkaline soil may lead to nutrient lockup, preventing plants from absorbing the necessary nutrients.
9. Soil pH and microorganisms
Soil pH also impacts the activity of beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients.
Maintaining a balanced soil pH helps create a healthy environment for these vital helpers in your garden.
10. Soil pH and pests
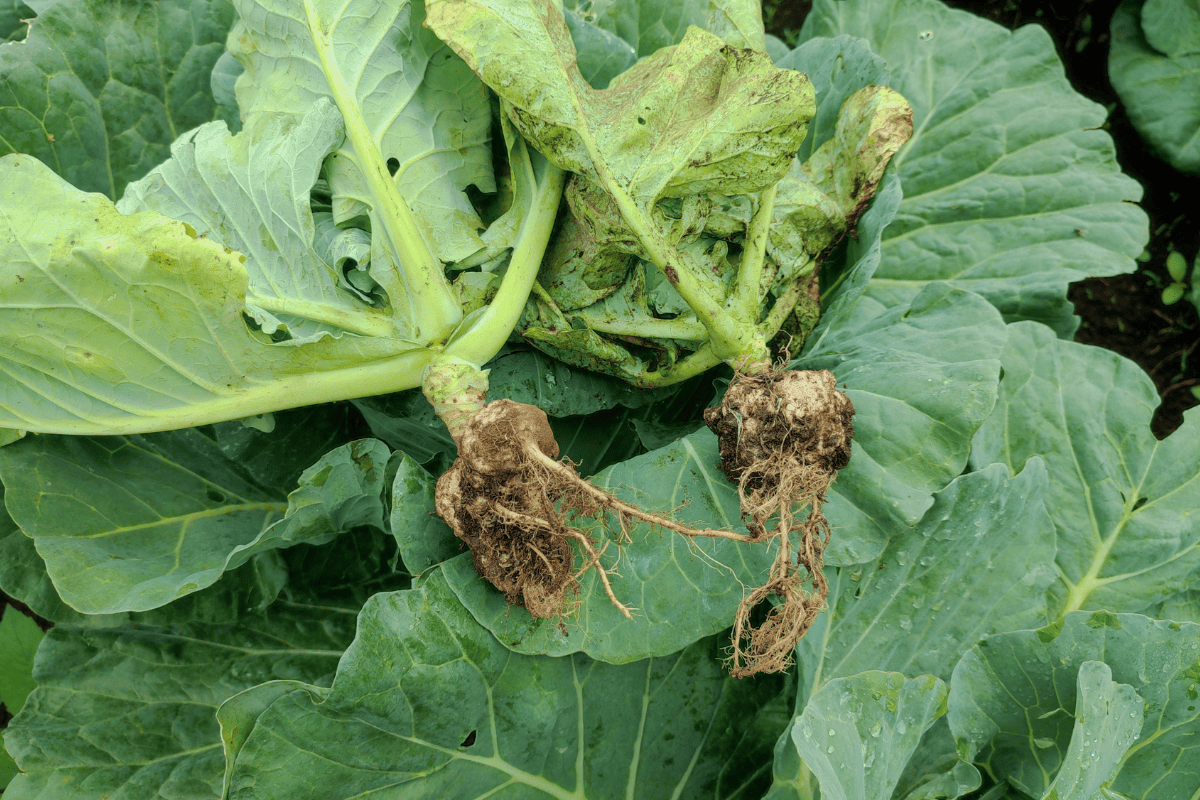

Some pests and diseases may thrive in specific soil pH conditions. For example, clubroot, a disease that affects brassicas, is more prevalent in acidic soil.
By managing your soil pH, you can reduce the likelihood of pest and disease issues.
11. The effect of fertilizers on soil pH
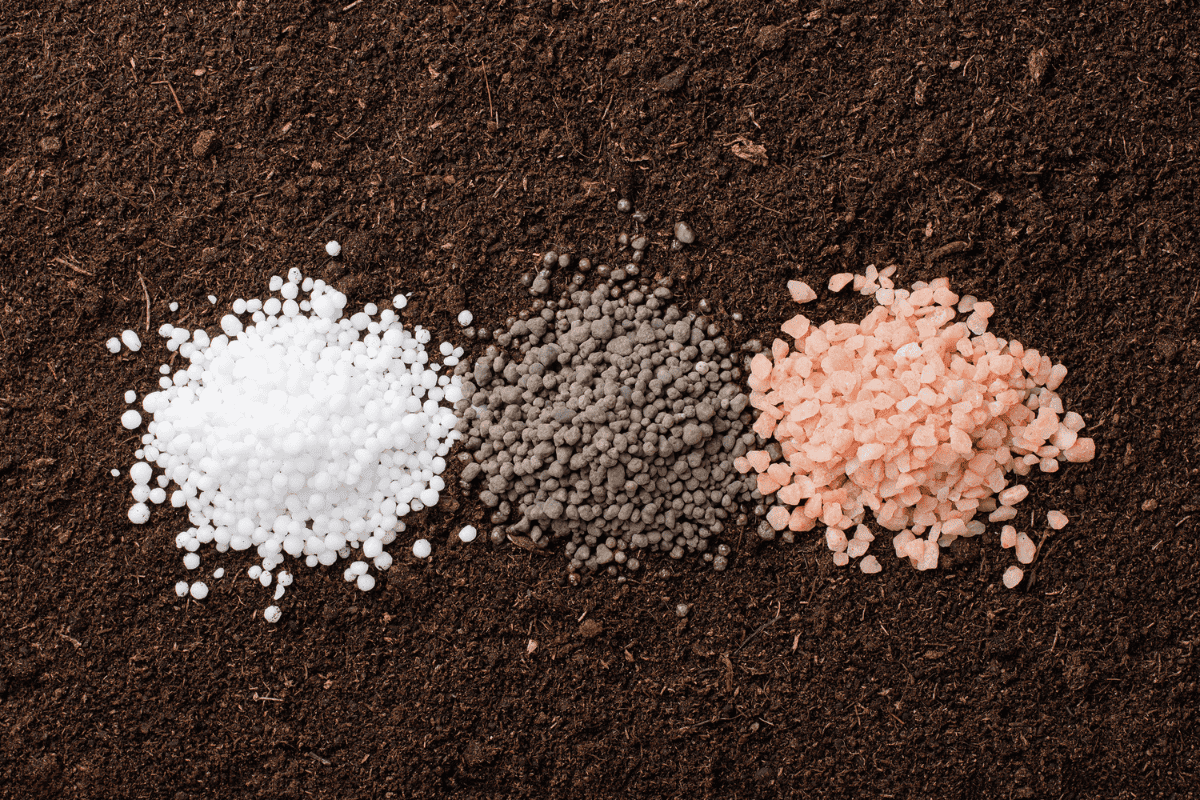

Some fertilizers, like ammonium-based nitrogen fertilizers, can acidify the soil, while others, such as lime and wood ashes, can make the soil more alkaline.
Be aware of the impact of the fertilizers you use on your soil pH and adjust your applications accordingly to maintain optimal conditions for your plants.
It's also essential to follow the recommended application rates and retest your soil pH after applying fertilizers to avoid overcorrection or nutrient imbalances.
12. Signs of pH imbalance in your garden
An imbalanced soil pH can manifest in various ways, such as stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or poor flowering and fruit production.
Suppose you notice these signs in your garden. In that case, it's essential to test your soil pH and take corrective measures to create a more hospitable environment for your plants.
13. Patience and persistence in managing soil pH

Adjusting soil pH can be a gradual process, and it may take time to see the results of your efforts. Be patient and persistent in monitoring and managing your soil pH. Your garden will reward you with healthy, thriving plants.
14. Determining the pH requirements of your plants

You'll need to know their specific pH preferences to create the ideal environment for your plants. You can find this information in gardening books, plant labels, online resources, or by consulting your local nursery or extension service.
Understanding your plants' pH requirements is crucial in maintaining their health and ensuring they have access to the nutrients they need to grow and thrive
15. How soil pH affects water quality
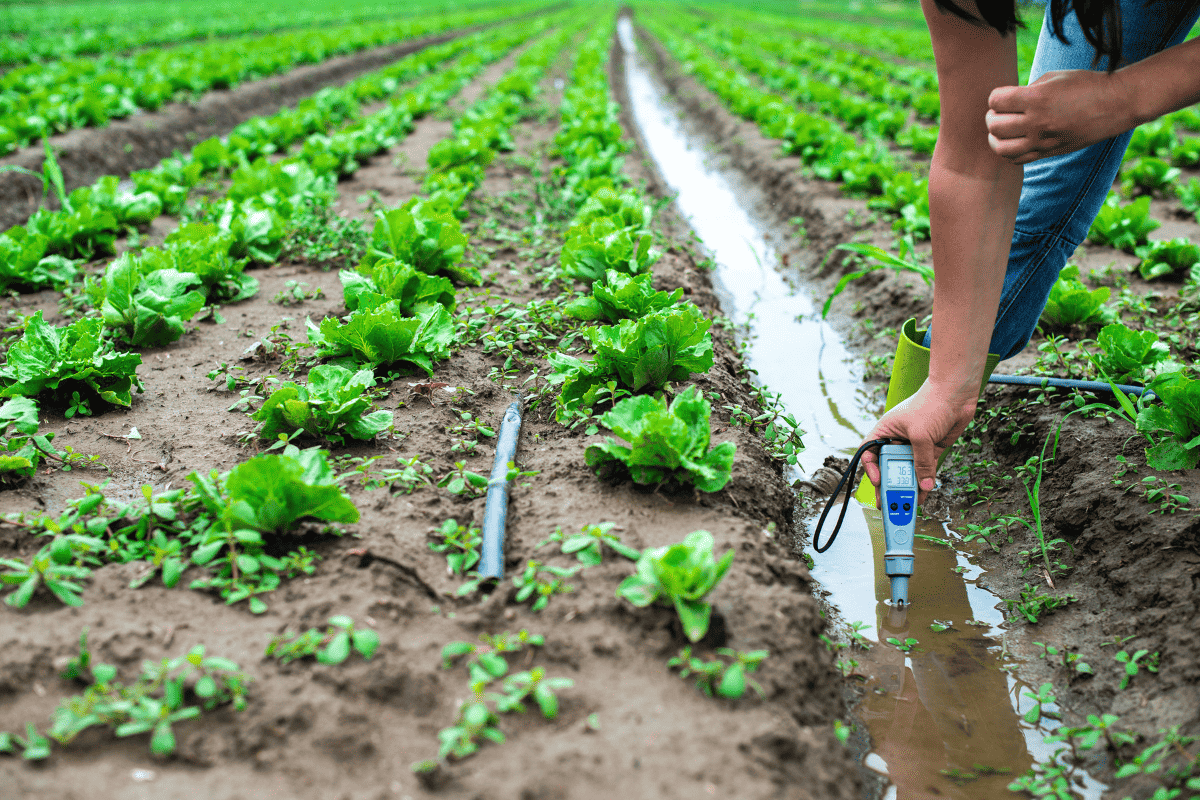

The pH of your garden soil can also impact the quality of water runoff, ultimately affecting nearby water bodies, such as streams, rivers, and lakes.
Acidic soil can leach heavy metals, like aluminum and iron, into the water. In contrast, alkaline soil can contribute to the growth of algae blooms.
By managing your soil pH, you not only support the health of your garden but also contribute to the health of the surrounding environment.
Ready for more to read? Here you go:
What Is The Best PH For Blackberries?
Seven Best Nitrogen-Fixing Cover Crops
Does Bay Laurel Prefer Acid Or Alkaline Soil?
7 Perennials That Thrive In Acidic Soil
Master Your Garden's Soil pH for a Thriving, Eco-Friendly Oasis
You're now ready to create a thriving, eco-friendly garden that caters to the unique needs of your plants.
By understanding the pH requirements of your plants, maintaining optimal soil conditions, and considering the impact on water quality, you're on your way to cultivating a vibrant, flourishing garden oasis.
Embrace the power of soil chemistry and watch as your garden bursts into life with a profusion of colors, scents, and flavors. Happy gardening!


