Various insects such as bees and butterflies pollinate flowers. This action is known to maintain balance in the ecosystem. Certain plants attract particular pollinators because of their distinct characteristics. With that being said, we have researched every aspect you need to know about bougainvilleas and bees.
Bees are not generally attracted to bougainvilleas because they cannot access the nectar available at the base of the flower. The elongated trumpet shape of the flower requires a proboscis that bees do not possess. Pollination is made possible by other creatures such as butterflies, moths, and hummingbirds.
In this article, bougainvilleas, bees, and pollination are discussed so that you will have a deeper understanding of how they interact and affect each other as well as the environment. Based on your inquiry, we will assume you have existing bougainvilleas and would like to propagate them or are interested in how to attract bees in general.
Bougainvilleas
Bougainvilleas, also called paper flowers, are attractive ornamental vines, bushes, and trees belonging to the Nyctaginaceae plant family. Sepal-like growths or bracts give the plant its distinctive colors of white, red, yellow, pink, and orange, while all flowers are small and whitish.
These plants grow mostly in areas with warm climates because it has high drought tolerance. The flower contains both the male (stamen) and female (pistil) reproductive structures. Although this is the case, these plants are not self-fertile; they need to be cross-pollinated with other bougainvilleas for them to produce seeds.

Common pollinators are butterflies, moths, and hummingbirds because they basically have a proboscis that will enable them to suck the nectar inside the trumpet-shaped or hollow flower of the bougainvilleas.
Bees do not pollinate this particular plant specie because they do not have a proboscis, and as such, they cannot access the nectar at the base or the ovary. The flowers of bougainvilleas do not have a scent, which is particularly important when attracting bees.
How To Propagate Bougainvilleas?

There are three ways you can propagate bougainvilleas: seedlings, cuttings, and layering. The latter two propagation methods result in the plant being a replica of the mother plant.
Through Cuttings Or Stem Fragments
The main principle of this method is cutting a thick 6 to 8 inches long stem from the mother plant, preparing, and placing or piercing it gently onto a pot filled with soil. If the stalk classifies as a hardwood (mature stem), add river sand and apply a rooting hormone to the potting mix.
Before placing them onto the mix, remove all the leaves on the lower portion of the stem. After planting, do not water them, instead, enclose them inside a Ziploc or plastic bag. This will function as a mini-greenhouse where moisture is retained, maintaining the ideal humidity level.
Put the pot in areas where it can get strong indirect light. Check the soil every 10 to 12 days. If dry, sprinkle or spray a small amount of water. It will take 7 to 10 weeks for roots to emerge. The growth of leaves is an indication that the roots are about to appear.
After light watering the cuttings for at least two weeks and giving them their sunlight requirements, you can now transfer them to a new pot. Remember to taper the plant's exposure to sunlight before transplanting them.
NOTE: Semi-hardwood cuttings are safe to propagate during summer, while hardwood stems have an increased chance of growing roots if propagated during winter or when temperatures are low.
Layering Method
The layering method refers to the asexual propagation of plants wherein a stem or stalk has to generate roots while still attached to the mother plant. It basically supplies the stem with water and nutrients whilst the roots are still growing.
To do this, make a diagonal cut in the stem and cover the area with moss and a plastic bag. This will act as its own greenhouse that will enable the roots to form. Bind together with a string. This process can take up to two months. Once the roots develop, you can now transfer them to a new pot.
Bees: Essential Pollinators
Bees are classified as winged insects and feed on the nectar and pollen of flowers which are their primary source of energy, protein, and other nutrients.
These insects are considered to be the most important pollinator on the planet, especially because they are vital in keeping a healthy and stable food supply, and they generally help in maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
A wide variety of plants that we rely on for food require to be pollinated, particularly by bees. These insects facilitate and increase nutrients of self-fertile growths such as oil seed crops and fruits. They also strengthen plants' resistance to harsh conditions and diseases.
They essentially pollinate about 80 percent of flowering plants all across the globe, including avocados, blueberries, and cucumbers.
As reported by Pollinator Stewardship Council, avocados' fruit yield increases by 350 percent when pollinated by honeybees and other pollinators. A general increase in cucumbers' production was also evident. These are just some significant examples that illustrate the importance of bees.
The disheartening fact about all of these is that in the United States alone, one-third of honeybees have died in the past few years. Scientists link the cause to habitat loss and to the use of a specific type of pesticides called neonicotinoids and other pesticides available across the planet.
How Pollination Works
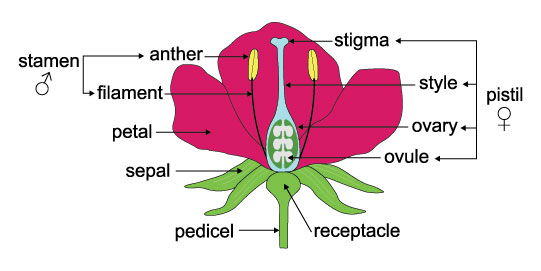
Pollination is the process of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. This method lets the plant produce a seed that is essential for reproduction. Pollens look like insignificant yellow dust which are integral in plants' reproductive cycle.
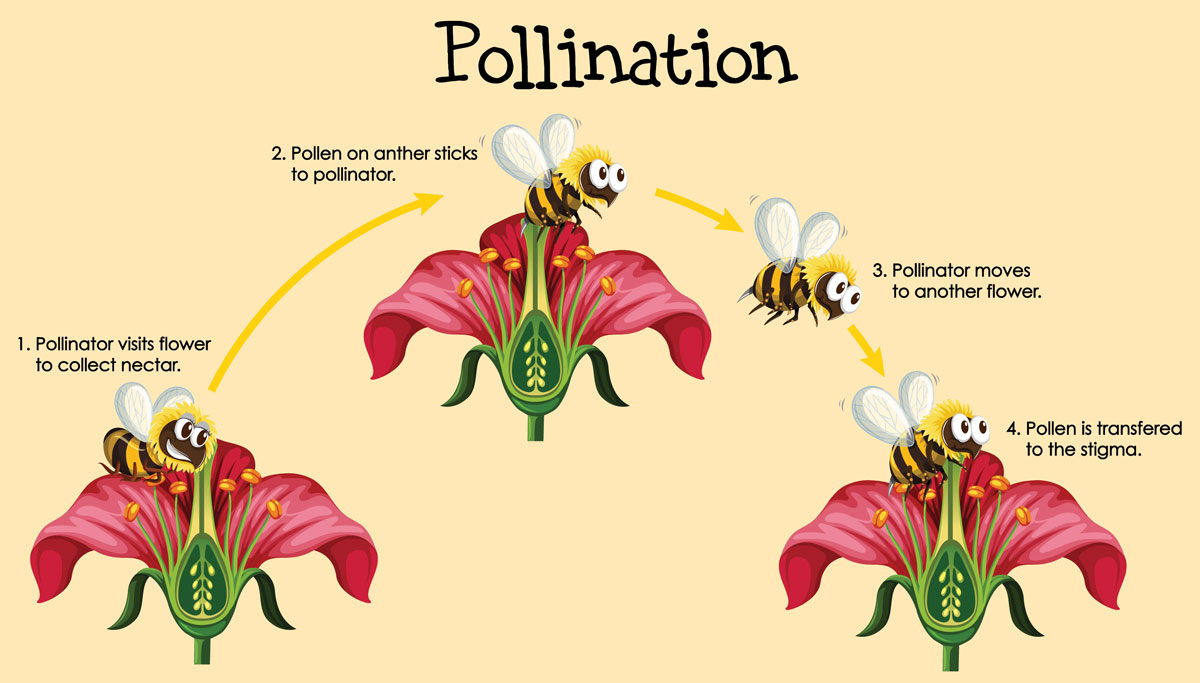
They are transferred through wind and insects such as bees, butterflies, and birds. When pollens are transmitted to another flower with the same specie, seeds will then be produced. These grains are located in the anthers of plants. When bees eat the nectars in flowers, pollen clings or adheres to their branch-like hairs called scopae.
Afterward, the vibration of their bodies whenever they fly causes these grains to fall off, passing them between plants, especially when they visit another flower, completing pollination.
In The Absence Of Pollination
Pollination is greatly essential in the survival of an ecosystem because the absence of such disrupts the ecological balance and causes a series of effects detrimental to the planet itself.
Effects On Water And Soil
Without pollination, flowering plants will generally dwindle or decline. There are 1600 species of crops in the world, and 80 percent of them depend on pollination to survive.
Flowering plants purify the air and help prevent erosion because their root system fastens or keeps the soil in place. Their leaves act as a cover that keeps rain from directly affecting the ground, and as such, protect it from being too moist and soft.
In general, the water cycle mainly depends on plants to release water vapor into the atmosphere. Without plants, soil erosion will be prevalent, and the cycle will be disrupted. These vegetation need pollination for their reproduction.
Effects On Carbon Sequestration
For the past century, there has been a significant increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere. This situation occurs because of the burning of fossil fuels and the devastation of forests.
Plants function as an instrument in carbon sequestration. During this cycle, they absorb carbon dioxide present in the air and combine it with other elements in order for them to make their own food.
In the absence of pollination, there would be no vegetation that could contribute to carbon sequestration.
Who Are The Pollinators?
Pollinators are animals responsible for transporting pollen from one plant to another. This helps complete the fertilization process of various flowering plants. They are classified into insects and vertebrates such as bees, pollen wasps, mosquitos, butterflies, moths, bats, birds, and some lizards.
Worldwide, there is a significant decline in the population of various pollinators mainly because of habitat loss, pesticides, diseases, and pests. This is a warning that the ecological balance is almost in the midst of destruction.
What Can We Do?
As human beings, we have the responsibility to restore this balance. There are several ways we can promote and protect our pollinators:
- Cultivating plants - particularly those that provide nectar or food for all pollinators
- Lowering usage of chemicals and pesticides
- Reducing our own impacts by using locally produced and organic food and following the three R's - Reuse, Reduce, and Recycle
What Flower Is A Bee Most Attracted To?
Growing plants that can attract pollinators, such as bees, should be one of your considerations when planning to cultivate or create a garden. Flowering plants, different vegetation, and fruit trees are a bee's major source of food.
Here is a list of plants that may interest you and that may keep the bees buzzing:
- Lavender
- Blue Borage
- Pussy Willow
- Lilac
- Crocus
- Goldenrod
- Bee Balm
- Chives
- Abelia (Bee Bush)
- Sunflower
In Closing

Bees are essential in maintaining an ecosystem and the survival of living organisms on the planet. We hope this article proved to be an eyeopener about the importance of pollination and pollinators. Happy gardening!
