Raised garden beds are an excellent way to grow small crops, vegetables, certain fruits, and flowers. The process entails certain procedures to create optimal growing conditions and maximize yield. If your raised bed seems to dry out too quickly, read on since we have researched ways to assist you in that regard.
The soil quality and composition of your raised garden bed is the primary reason it dries out too quickly. There may not be enough material to retain moisture over a prolonged period, so the water either drains or evaporates. A combination of organic compost and mulch would maintain and regulate hydration.
Raised beds allow gardeners and enthusiasts to grow plants in limited or irregular areas. Since they are confined and demarcated, maintenance is relatively easy, and the vegetation is not prone to damage. The preparation, soil content, ideal plants, care, and other aspects of the process are included to help you create a productive garden bed.
Reasons Raised Beds Dry Out And How To Prevent It
The soil structure and composition determine its capacity to retain moisture and provide enough hydration to sustain the plants. If the material is too compact, water may not penetrate the surface and simply flow off to the sides.

Loosen the soil through tilling and add compost and inorganic materials like sand and crushed gravel into the mix to make it more porous. This would improve water absorption and increase the garden bed's moisture.
The height of the bed could also cause it to lose water quickly. Since it is elevated, and the sides are exposed, evaporation occurs faster if it is too shallow. This occurs especially during the summer.
Ideally, a raised garden bed should be six to eight inches high for it to hold enough water over a sustainable period. This would also create a stable base and adequate space for the roots to develop.
If you live in warmer climates, you might notice that the topsoil is always parched or dry despite regular watering. This occurs especially if the raised bed is located in the open and exposed to full sunlight.
Apply two to three inches of mulch on the bed's surface evenly, covering all areas.
A mixture of dried leaves, wood chips, twigs, and peat moss would help regulate the soil temperature and retain moisture. While it decomposes, the mulch will slowly release nutrients into the soil, which would benefit the plants.
What Are Raised Garden Beds?

Raised beds are elevated plots used for growing fruits, vegetables, and other plants. Gardeners and enthusiasts can modify or use a potting mix ideal for their chosen vegetation or variety.
The gardening medium generally improves soil composition and drainage, and it optimizes the plants' health and productivity by preventing the weeds from proliferating.
Check out Miracle-Gro Raised BedPotting Soil on Amazon.
Types Of Raised Beds
There are three forms of raised beds – raised ground, supported, and containerized. If you intend to make one, you must determine which type is best suited for your area or garden.
Raised Ground Beds
A raised ground bed is the most basic type of planting bed that is usually six to eight inches high. To create one, all you need is additional soil – either from the surrounding area or from your own potting mix that is tilled to make a mound.
If the soil is too compact and not ideal for planting, use a mixture of compost, peat moss, and animal waste in your own garden mix. When creating the bed, remember to taper down the sides to a 45-degree angle to maintain the ideal shape of your raised bed.
Supported Raised Beds
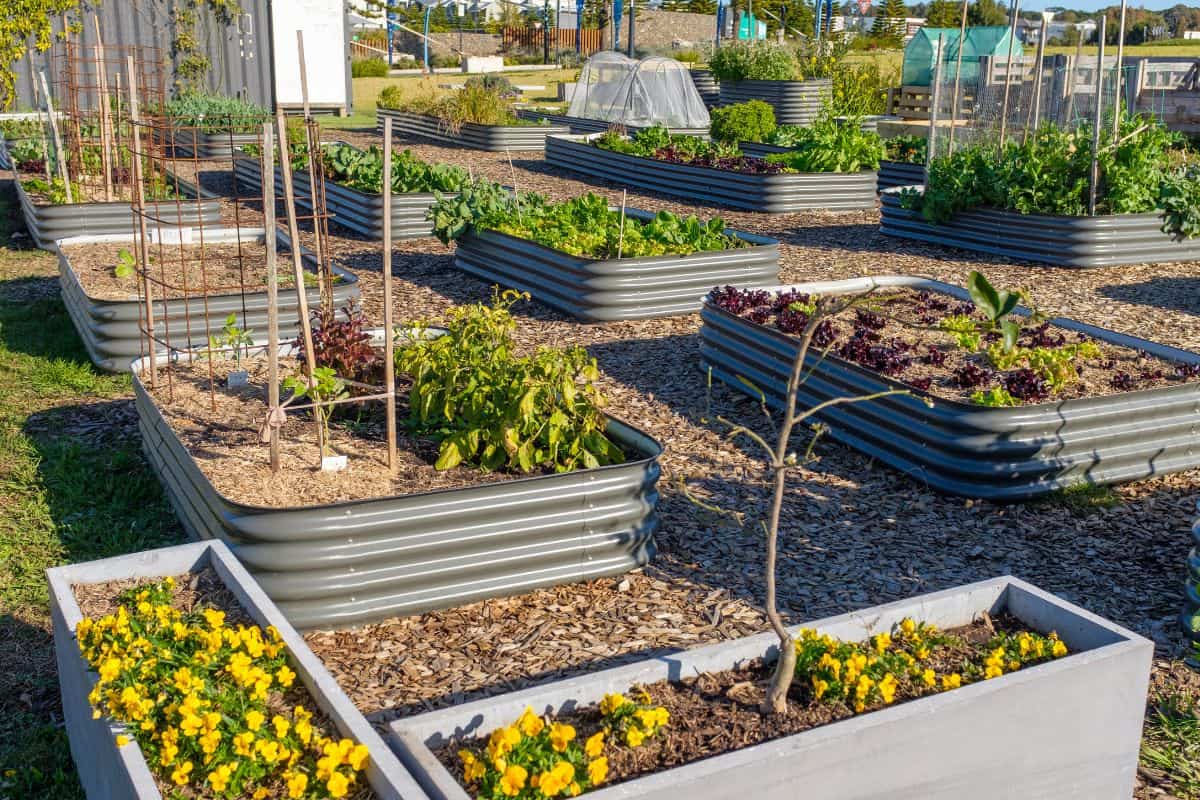

A supported raised bed, as the name implies, is created by placing a barrier or a garden edger around the sides of the bed that acts as a support and barricade to protect the plants from weeds.
It helps in maintaining the shape of the plot and prevents gardeners from stepping on it. You can either use plastic, metal, stones, or bricks as your in-ground garden edger.
Since supported raised beds feature barriers that surround the plot, they may be designed to be higher or wider than your ordinary beds. You can use wooden planks to traverse opposite sides and be able to reach the plants towards the middle part of the structure.
Check out Galvanized Raised Garden Bed Kit on Amazon.
Containerized Raised Beds
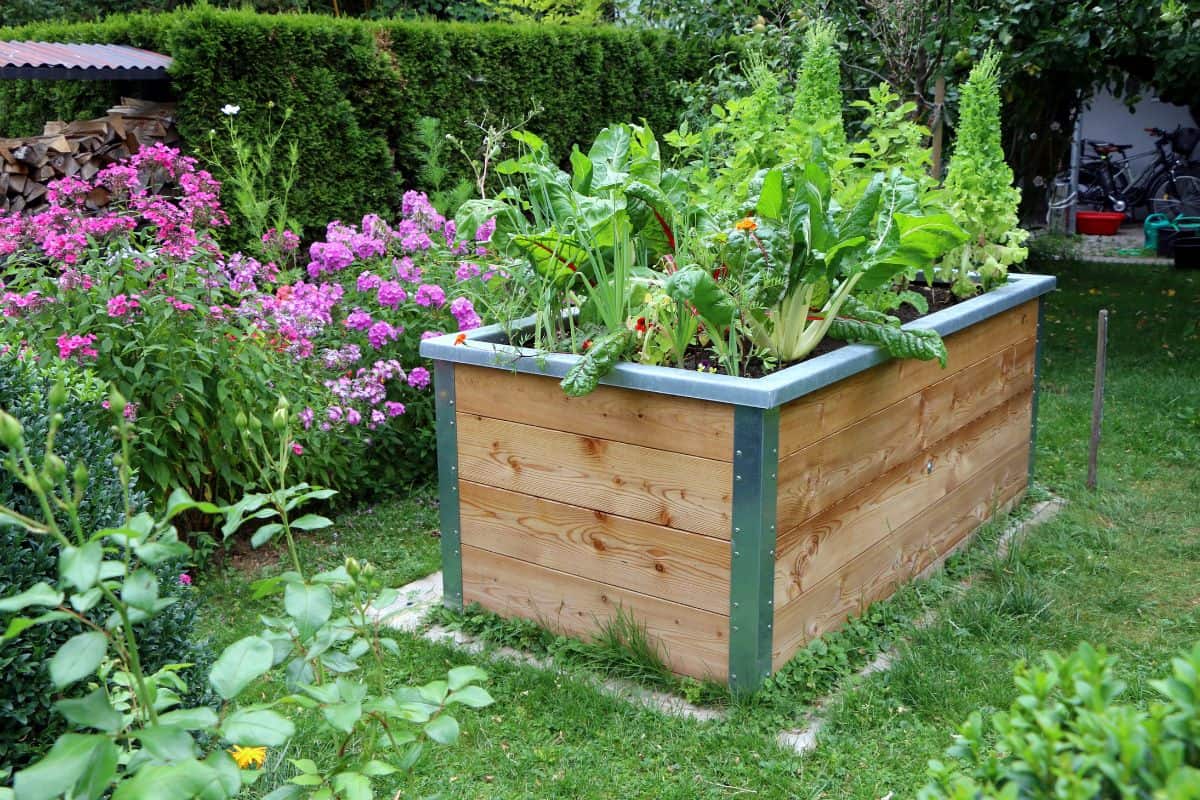

Containerized raised beds feature the highest and most elevated type of bed since they have a height of 10 to 12 inches.
They are ideal for limited spaces since they maximize the planting medium which allows you to cultivate flowers and vegetables within the constraints of the available space.
When creating your bed, choose a height most suitable for you, and remember to build a container using materials that do not decompose over time, such as metals, plastics, stones, concrete, or rubber.
Key Considerations When Creating A Raised Bed
Plan the general layout of the raised bed based on the available area you intend to occupy. Consider the number, size, location, spacing, and other factors before actually laying down the soil.
Size And Number Of Plots
The total available area would determine the number and dimensions of your raised garden beds. The width should be so designed in a way that the plants are accessible for watering, pruning, fertilizing, and eventually, harvesting. If it is possible to go around the plot, three to four feet would be an ideal width for the bed.
Spacing
Adjacent beds should be at least two feet apart to provide enough walkway between plots. You could easily maneuver a wheelbarrow, watering cans, or crates without damaging the vegetation.
This would also create adequate space for tending to the beds like weeding, mulching, and other forms of maintenance.
Location
Most gardeners and enthusiasts prefer to cultivate and raise vegetables or flowers that require full sunlight. Placing beds under trees or any form of canopy would affect the growth of the plants. Select areas and locations that provide optimal conditions that would support your chosen and preferred species.
Drainage
Before laying down the soil, determine the density of the ground it would settle on. If it is too compact, an underlay may be necessary to improve drainage.
Add a layer of pebbles or crushed gravel about an inch or two to prevent water from pooling under the raised bed. This would also control weed growth and protect the roots from rotting.
What To Grow In Raised Beds
You can grow vegetables individually or as companion plants. The important thing is to know which varieties thrive and grow alongside each other.
To illustrate, let's consider growing lettuce. It is suggested to plant turnips in between the rows of your lettuce because the former naturally repels slugs that will otherwise eat the leaves of your growing vegetables.
On the other hand, planting an alyssum will actually attract beneficial insects such as hoverflies since they feed on aphids - the number one pest that generally destroys a lettuce garden.
Raised Beds Vs. In-Ground Gardens: A Brief Comparison
Raised beds and in-ground gardens are both used in agriculture as a medium for planting a variety of crops. Although they have similar functions, they differ in the way they are formed or designed.
The former is an elevated plot that uses a different soil composition. Raised beds are ideal in small spaces because they are easier to manage, they protect the vegetation against damage from foot traffic, and they can regulate soil temperature which allows for a longer growing period.
An in-ground garden is a flat planting medium more suitable for a larger area. You can directly grow vegetation on the ground without the need to create a mound. This makes it a relatively less cost consuming option.
Unlike a raised bed, the plot does not easily dry out, so less water maintenance is required. Irrigation systems are easier to design and install since you do not need to create a special arrangement as compared to a raised plot.
Both planting mediums have their advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right garden design is up to your needs. Be sure to use one suitable to your location and garden space.
How Do You Keep Water In A Raised Bed?
Aside from those mentioned above, you can install soaker hoses around your raised garden bed. The equipment is specially designed to gradually distill water onto the elevated plot. Connect the hose near a faucet or any other water supply for easier access.
Do Raised Garden Beds Need More Water?
Since raised garden beds have the tendency to dry out quicker, especially in arid regions, they may need to be hydrated more often as compared to a regular garden plot.
Always remember to use proper soil composition, add a layer of mulch, and install a proper irrigation system to keep the potting mix moist as needed.
In Closing
Raised garden beds are being used by gardeners and plant enthusiasts alike. Even though the medium dries out quicker, there are relatively simple ways to remedy the problem. We hope the article helped you keep your elevated plot from drying out. Happy gardening!
You might also find these topics informative:


