 Gardening requires an understanding of the basic nutritional requirements of plants. One of these vital nutrients is nitrogen. Understanding what nitrogen is and how a plant uses this nutrient can mean the difference between lush, healthy plants, and sickly ones. We've done the research to bring you a concise explanation of how plants use nitrogen.
Gardening requires an understanding of the basic nutritional requirements of plants. One of these vital nutrients is nitrogen. Understanding what nitrogen is and how a plant uses this nutrient can mean the difference between lush, healthy plants, and sickly ones. We've done the research to bring you a concise explanation of how plants use nitrogen.
Plants use nitrogen to grow strong stems and leaves. Different types of plants may use more or less nitrogen depending on their needs.
Keep reading for more details on how plants use nitrogen so you can master this important aspect of gardening.
What is nitrogen?
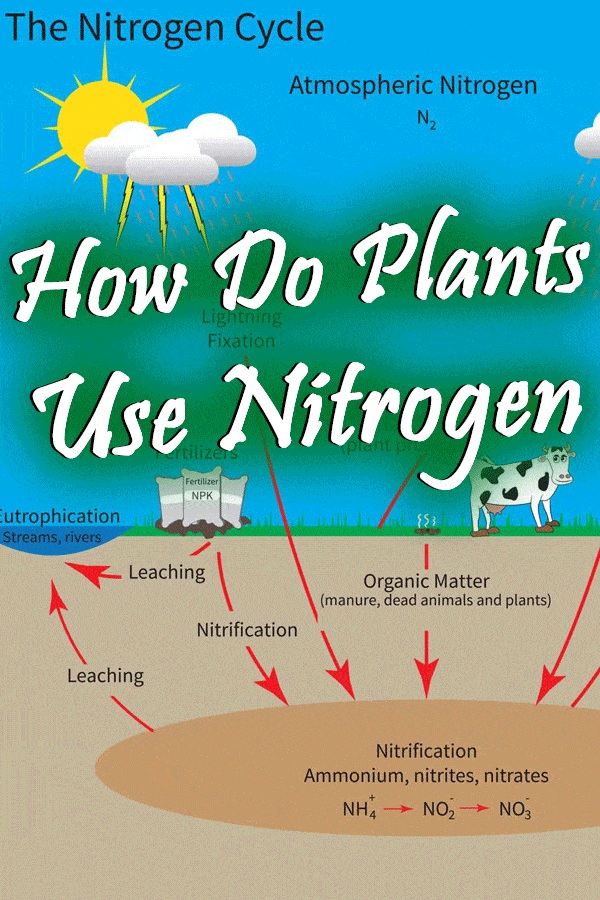
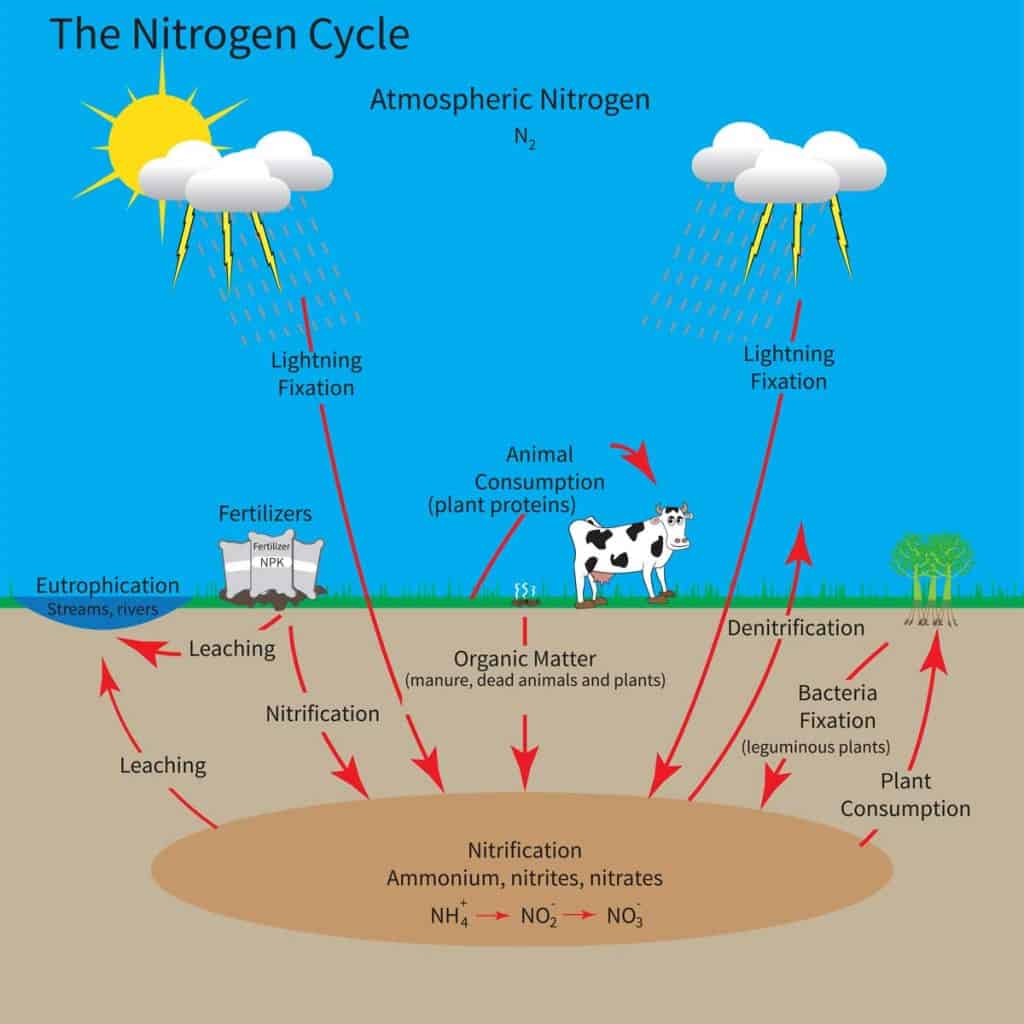
Nitrogen is an essential element not only for plants but for all life. Nitrogen found in abundance in the air. Unfortunately, plants cannot take it directly from the air.
Nitrogen gas is converted to a usable form for plants by nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil, which is found in abundance around legumes like alfalfa, peas, clover, and beans. This process is called nitrogen fixation.
Some plants, like the one listed above, add nitrogen to the soil, while others use more than usual, like pumpkins and squash. It is important to know what your individual plants' needs are, so make sure that you do your research before you start amending your soil.
Why is nitrogen so important for plants?
Nitrogen is the primary nutrient that plants need to grow a strong stem structure and lush green leaves. Strong streams allow plants to grow big and hold more fruit. Lush green leaves not only make your plants look healthy but they are vital to capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
Without good access to nitrogen, plants will grow weak. They will not be as full as healthy plants, growing fewer stems and leaves. This will lead to less fruit and vegetable production. The fruit produced may not be as sweet. Plants may fall over easily. Low nitrogen levels will cause overall growth to be stunted.
How do you know if there is a problem?
Leaves turning light green or yellow is the classic sign that nitrogen levels are too low. The color change will start at the tip of the leaves and move towards the stem. The yellowing will affect the lower, older leaves first.
You may also notice that your plants are not growing as big or as fast as expected. Fruit and vegetable production will be low.
An Easy Fix
Nitrogen levels in your plants can be corrected quickly by adding nutrients to the soil. The first number on a fertilizer bag represents the percentage of nitrogen in the fertilizer. So a bag with 12-10-5 has 12% nitrogen.
If your plants are showing signs of low nitrogen levels use a quick release fertilizer that is high in nitrogen. Your plants will recover quickly.
However, too much of a good thing can be bad. Adding too much nitrogen can cause the plants to have “ nitrogen burn”. This will cause stress to the plants and can cause them to die. So follow the instructions on the fertilizer. Always start with the lowest recommended amount and see how your plants react.
Natural Ways to Keep Levels Healthy
Composting is a great way to add healthy nutrients to your soil. The breaking down of foodstuff and animal manure causes the chemical reactions that are essential for nitrogen fixation. Adding compost to your soil will give your plants a steady, slow release of nitrogen that will ensure good health.
Planting cover crops is another great way to have nitrogen-rich soil if you have space. Plant an area with a legume like alfalfa. When it dies off, allow it naturally decay into the soil then plant your vegetables on top. The nitrogen-rich soil will be perfect for pumpkin or other types of plants that are heavy feeders.
Use Your Knowledge Wisely
Now that you have an understanding of how plants use nitrogen, and how to make sure they have what they need, you are ready to get growing. Just remember to follow the directions on the bag of fertilizer, and when in doubt about what your specific type of plant needs, research it!
