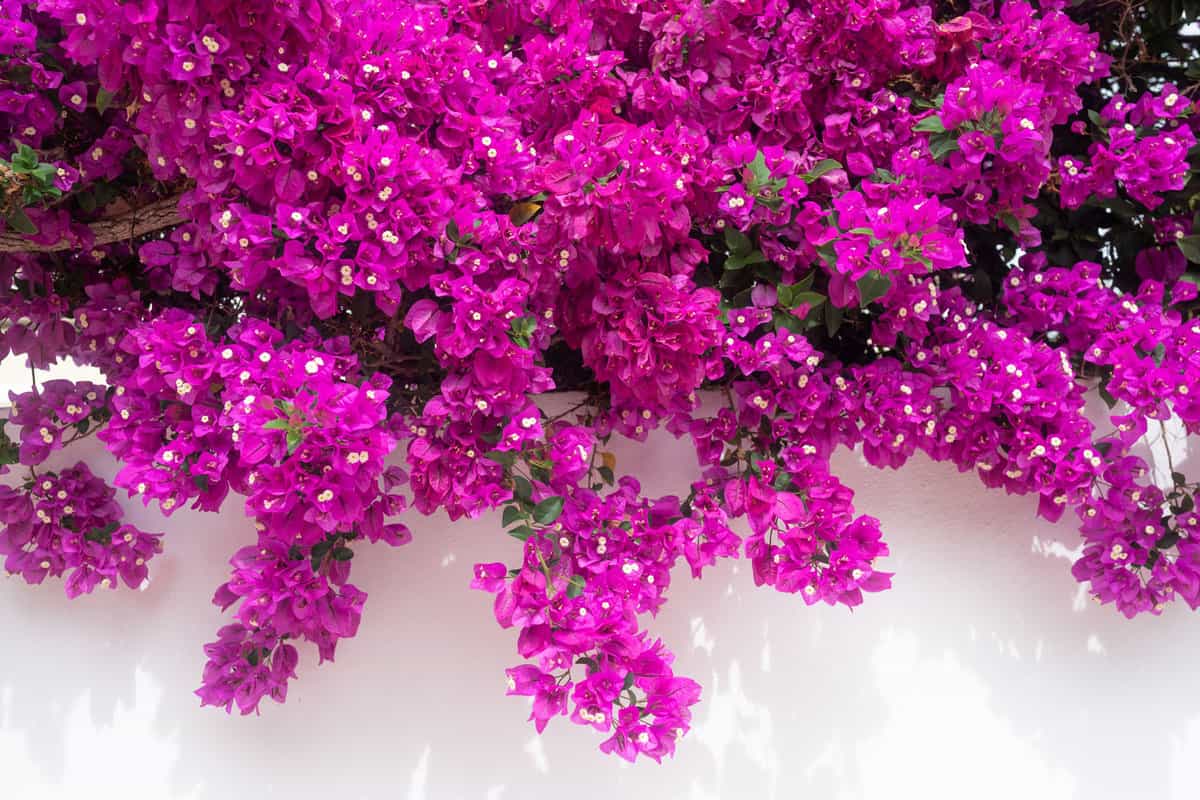
Bougainvillea is a popular tropical plant known for its vibrant and colorful bracts that can bring life to any garden.
While it's admired for its beauty, some gardeners might wonder if its roots are invasive, causing potential damage to structures and competing with other plants in the vicinity.
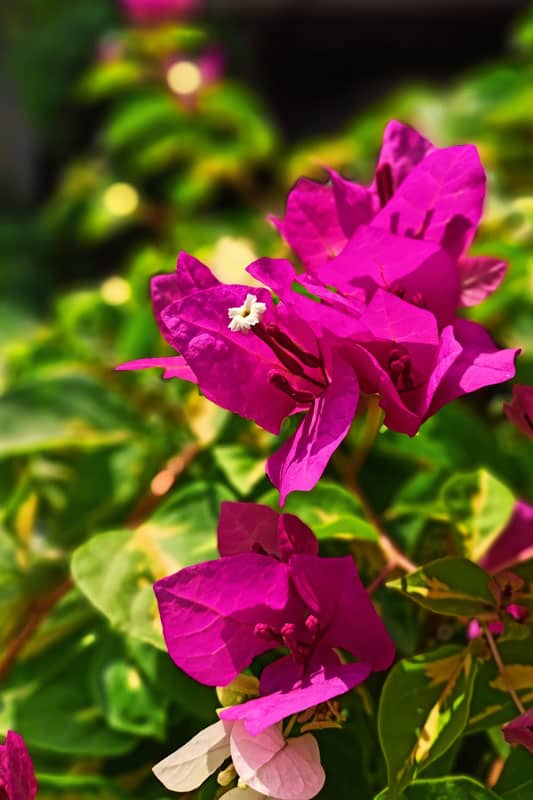

To address this concern, it's important to understand the growth habits of bougainvillea.
Before adding this plant into your landscape or garden, it's important to familiarize yourself with its growth habits and potential management strategies to ensure a healthy environment for the surrounding plants and structures.
Bougainvillea's Root System
In general, bougainvillea roots are considered non-invasive, as they have a fine and delicate root system. However, it still has a tendency to be invasive.
When planting a bougainvillea, keep in mind that it can require a significant amount of space to grow properly.
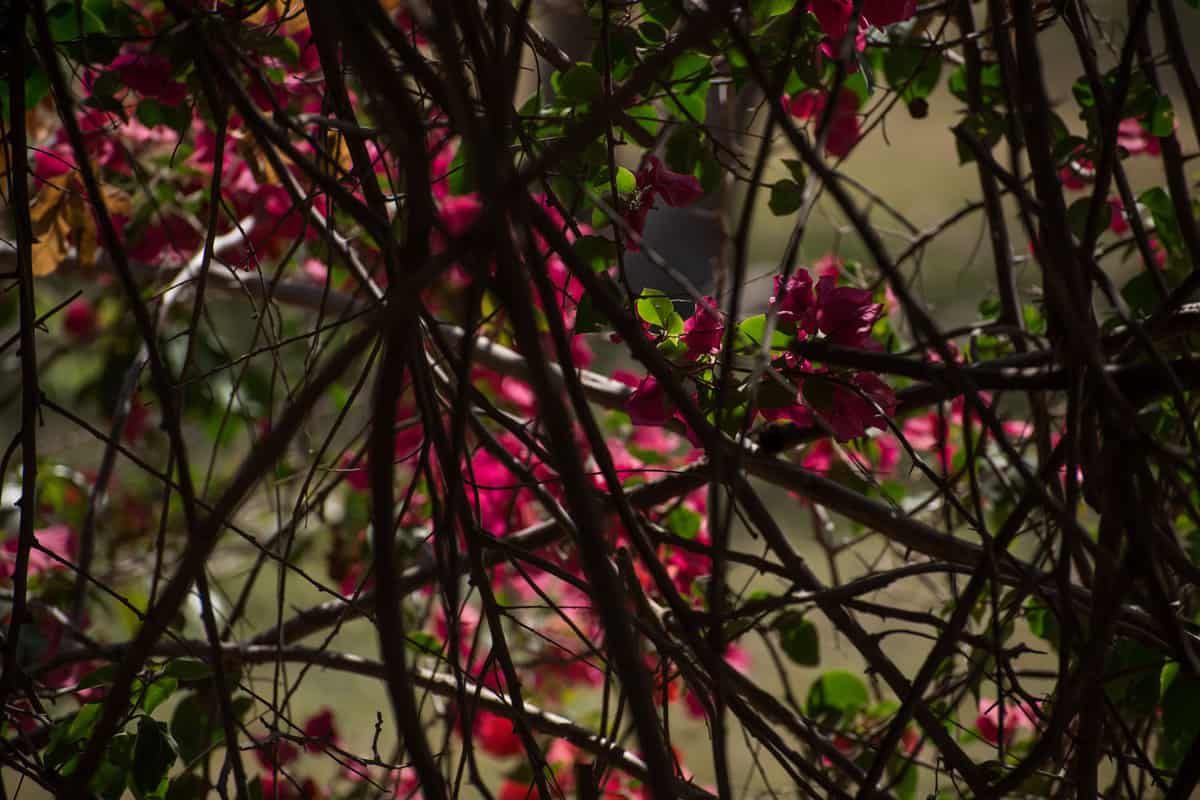
It prefers moderately fertile, organically rich soil that retains moisture but is not soggy.
As such, provide adequate space and proper soil conditions to ensure a healthy, non-invasive growth.
While bougainvillea roots are generally non-invasive, be cautious when planting near structures or other valuable plants.
Giving your bougainvillea the optimal conditions to thrive will not only result in a beautiful display of vibrant colors but also help to maintain the integrity of your landscape.
Growth Patterns
Bougainvillea roots are generally not considered invasive because they tend to remain relatively shallow and confined near the base of the plant.

Typically, these roots stay within the first 12 to 18 inches of soil and do not spread far beyond the plant's canopy.
Impact on Soil
Although bougainvillea roots do not pose a significant threat to the surrounding soil structure or other plants, consider the potential impact they might have on their immediate environment.
Since bougainvillea prefers sandy or loamy acidic soils with good drainage, planting them in such conditions will minimize the likelihood of damaging neighboring plants and soil structures.
Additionally, bougainvillea is tolerant of drought, heat, and salt, making it a relatively low-maintenance plant when planted in the appropriate environment.
Effects on Built Structures
Bougainvillea has a fine root system, which makes it less likely to cause significant damage to hardscaping and other nearby structures.
The plant thrives in good drainage, so while the roots may expand in search of water, they are not nearly as aggressive as those of some other plant species.

That being said, it is still essential to consider the plant's placement in your landscape.
If planted too close to a building or other structures, the roots could potentially cause problems over time, especially if proper care and maintenance are not provided.
To minimize any potential risk, ensure that you provide adequate space for bougainvillea to grow and thrive.
This means planting it a safe distance from foundations and other structures where roots might cause concern.
Provide proper care such as regular watering, fertilizing, and pruning in order to help keep the plant healthy and its roots contained.
Cultivation Advice
When growing bougainvillea, keep a few things in mind:
- Plant it in a location that receives full sunlight, as it requires at least 6 hours of sunlight per day to thrive.
- Ensure it has well-draining soil to prevent root rot.
- Be gentle when transplanting, as the roots of bougainvillea are brittle.
Preventing Root Invasion
While bougainvillea is not considered invasive in the same way as some other plants, take steps to prevent the roots from causing issues in your landscape.

To minimize the risk of root invasion:
1. Maintain Regular Pruning
Managing the root system of bougainvillea can be effectively achieved by regular trimming of the stems.
After the plant has completed its flowering cycle in the summer, prune back the stems to remove old blooms.
This not only offers a chance to reshape the tree and remove any unruly branches but also helps limit the root system.
By restricting the size of the stems, you consequently reduce the expansive root system the plant requires for absorbing necessary water and nutrients.
Read more: How To Keep Bougainvillea Small
2. Opt for Container Gardening
Both dwarf and full-sized varieties of bougainvillea can be successfully grown in pots. Use premium potting soil and regularly trim the plants to maintain the desired size.

It's even possible to grow bougainvillea as bonsai, a testament to their hardy nature and tolerance to rigorous pruning.
3. Choose Dwarf Varieties for Compact Growth
Dwarf varieties of bougainvillea are an excellent choice for smaller spaces and for keeping the roots contained.
Capable of being maintained at a few feet high, these dwarf varieties can be trained up a garden screen. Their naturally smaller root systems correlate to the fewer stems they support.
In Closing
While bougainvillea's bright and colorful blooms are a beautiful addition to any garden, understanding the plant's root system and growth patterns is crucial.
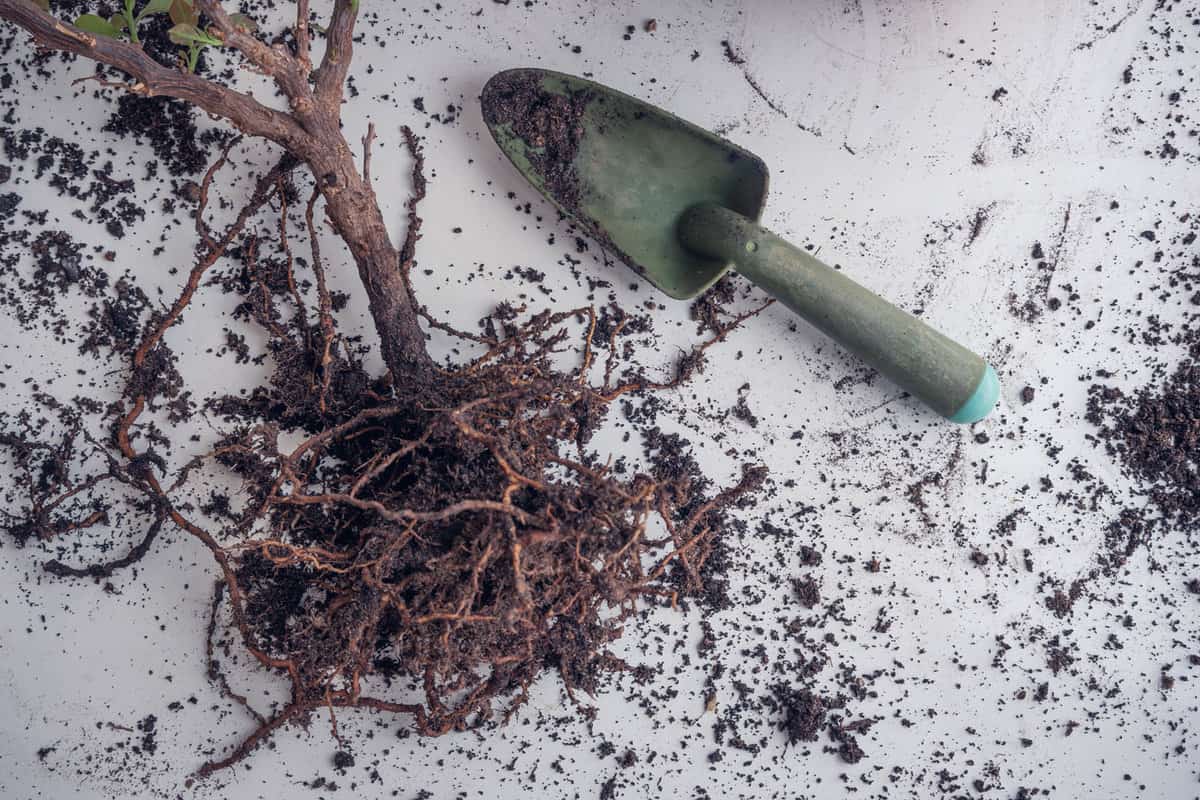

Despite having a non-invasive root system, it's important to take precautions when planting bougainvillea, particularly near other structures or plants.
Strategies like regular pruning, opting for container gardening, and choosing dwarf varieties can help manage bougainvillea's growth effectively.
The key to cultivating bougainvillea successfully lies in understanding its growth habits and managing them appropriately.
Read more about invasive roots:
