Pest infestations are the most common problem gardeners and plant enthusiasts experience. Several bugs feed on and harm vegetation - whiteflies and mealy bugs are the best examples. We have researched their differences to help you distinguish between these two pests.
Whiteflies and mealy bugs are common insect garden pests that are closely associated. They differ mainly in that mealy bugs crawl and infest all parts of a plant, including the root system. Whiteflies are winged, capable of flight, and limit their presence on the underside of leaves.
The article includes a comprehensive discussion of the similarities and differences between whiteflies and mealy bugs in terms of their appearance, preferred growing conditions, effects on plants, and the ways to control as well as prevent infestation.
How Do Whitefly And Mealy Bugs Differ In Terms Of Appearance?
Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae)
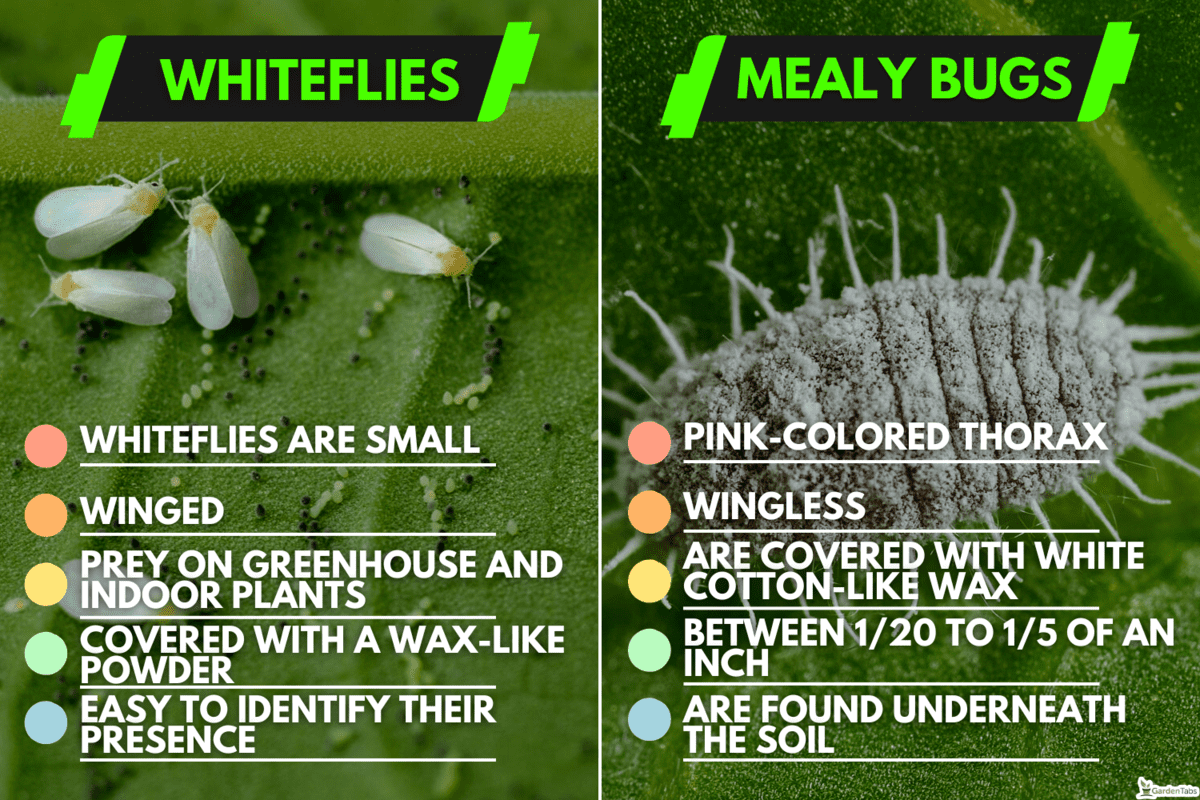
Whiteflies are small, winged insects classified as true bugs closely related to scales, aphids, and mealy bugs. They are a common pest that thrives in warm weather, causing damage to garden plants and crops on a considerable scale. In colder regions, they prey on greenhouse and indoor plants.
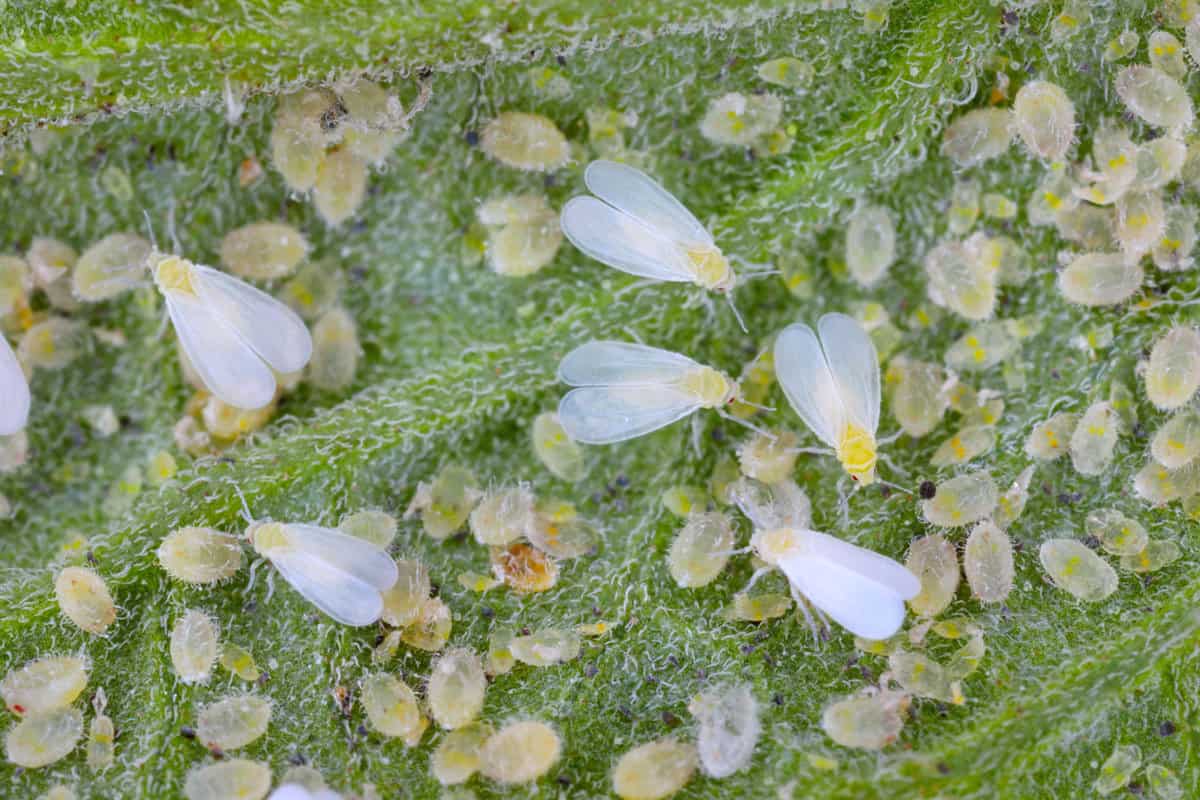

They closely resemble moths and flies but belong to a different class of insects. Whiteflies are covered with a wax-like powder that serves to protect their fragile exterior. They infest plants in clusters or swarms, resulting in a quick deterioration of affected growths.
It is easy to identify their presence since whiteflies hover, then scatter off once the host plant is disturbed by wind or watering. However, they are difficult to control and eliminate because they tend to resettle and proliferate rapidly.
Mealy Bugs (Pseudococcidae)

Closely related to whiteflies, mealy bugs are wingless insects with over 300 species found all across America. Different classifications can be identified by looking through their hinds and tails.
Although these insects have a pink-colored thorax, they appear to be white or gray because their bodies are covered with white cotton-like wax, which acts as a protective coating. They are small critters with a size range between 1/20 to 1/5 of an inch.
Mealy bugs extract nutrients from plant tissue and excrete a substance high in sugar, known as honeydew. Ants feed on this substance and tend to protect the mealy bugs from other predators because of this symbiotic relationship.
Ground mealy bugs are found underneath the soil and around the root ball. They extract nutrients from the plant’s root system.
What Attracts Whiteflies And Mealy Bugs?
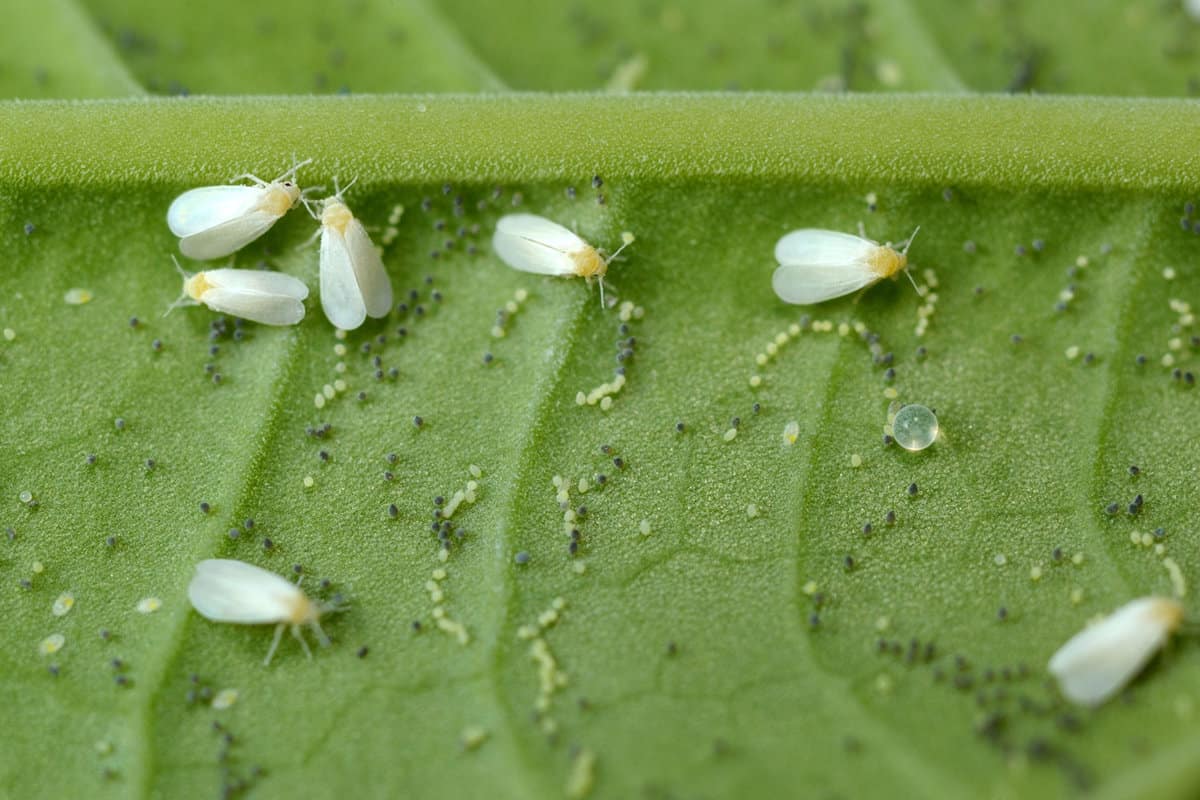

Whiteflies Prefer Lush Foliage
There are numerous species of whiteflies, and those present in warmer climates infest both indoor and outdoor plants.
They usually begin to reproduce and proliferate during mid-summer when the environment gets warm and humid. During this time, the adult females lay eggs on the underside of leaves, which hatch and produce larvae in two weeks.
Since the eggs tend to go unnoticed, the presence of whiteflies only becomes evident when the leaves show signs of infection. Trees, flowering plants, crops, ornamentals, and most other growths become hosts to infestation.
Dry, hot weather can cause dehydration and water stress on plants, making them more susceptible to whiteflies. Drought and heat are favorable for their reproduction, and the damage is most demonstrable during summer.
Whiteflies actually thrive when insecticides are applied during late spring and early summer. Natural predators such as beetles, ladybugs, dragonflies, and spiders are eliminated together with beneficial pollinators such as butterflies and bees. In the absence of other insects, whiteflies multiply more rapidly.
Whiteflies are attracted to thick, lush foliage, and newly fertilized plants become a natural target for infestation. Nitrogen promotes leaf growth and development, which is ideal for hosting whiteflies and increasing their reproduction.
Mealy Bugs Thrive On Stems & Leaves In Humid Climates
Mealy bugs are tropical insects that can be found mostly on perennial plants and thrive in humid as well as damp conditions. They are particularly attracted to plants that have high nitrogen content.
You can find them in the stems underneath the foliage, on the base of the plant, and its roots. Look for curled leaves since it is where the insects lay their eggs.
How Do They Affect And Damage Plants?
Whiteflies: Vectors Of Disease
Whiteflies infest a wide variety of plants, including citrus and other trees, warm-season vegetables, garden, and houseplants. Interestingly, they only feed on the leaves and do not generally affect the other structures.
More specifically, lemon, mulberry, fig, ash, privet, and fig and palm trees are notably susceptible. Infestations are common in tomatoes, eggplant, pepper, sweet potatoes, and cabbage.
They feed on ornamentals, gardens, and houseplants such as poinsettia, begonia, hibiscus, philodendron, pothos, anthurium, fennel, yarrow, and clover, to name a few. Essentially, they can infect most plants that have broad enough leaves to accommodate and host the eggs and feed the adults.
Whiteflies and mealy bugs attack plants in small swarms and extract nutrients from the leaf's tissue with their proboscis, a hairlike piercing organ equivalent to a mouth.
They feed on simple carbohydrates present in the foliage and excrete a clear, sugar-rich liquid known as honeydew. The substance promotes the formation and growth of sooty mold fungi that eventually reduce and block the plant's ability for photosynthesis.
The leaves turn yellow, wilt, and fall off prematurely causing the plant to weaken since there is inadequate production of food and nutrients. Ants and other insects which feed on honeydew may contribute to the plant's deterioration.
While their initial mode of infestation weakens and eventually kills plants, whiteflies cause more damage as vectors of diseases.
Bacteria and other parasitic organisms are caught and attached to the waxy substance on the whiteflies' exterior and are transferred to other plants when the swarm moves to other areas.
Mealy Bugs: Mild Attackers
Mealy bugs are particularly attracted to plants that are rich in tissue fluids. Fruit trees, including citrus and mango, are most susceptible to infestation.
Mealy bugs commonly feast on:
- Succulents such as aloe vera, agave, and echeveria
- Vegetables such as cabbage, cucumber, lettuce, asparagus, and beans
- House plants like African violets, begonias, orchids, jade, palms, philodendrons, poinsettia, and pothos
The effects vary depending on how severe the infestation is. A mild attack does not often harm plants. However, in more advanced cases, affected vegetation can die.
They are known to attack all plant parts, namely the leaves, roots, fruits, and flowers.
A mealy bug infestation causes a decline in plant growth and weakens its health. Apart from the appearance of white cotton-like figures on stems, foliage, plant base, and root ball, yellowing leaves and eventual fruit and leaf drop are common symptoms occurring on infected vegetation.
The honeydew secreted by mealy bugs promotes a natural breeding environment for fungi. Once sooty mold develops, fruit quality as well as plant health are affected.
How To Get Rid Of Whiteflies And Mealy Bugs?
Whiteflies
Whiteflies are more difficult to control and eliminate since they develop resistance to chemical pesticides, and repeated application only increases their tolerance. Natural methods and homemade remedies are more effective and less toxic to the environment of surrounding plants.
The proliferation of whiteflies can be minimized if their natural predators are present in the ecosystem. To make this possible, avoid using pesticides before summertime and limit their application before winter.
Beneficial insects and pollinators will survive to naturally maintain the balance and limit infestation.
You can spray a mild solution of soap, neem oil, and water into the foliage to coat and protect the leaves from whiteflies. The application would repel mature species and limit the survival of laid eggs since it would interfere with their preferred habitat.
However, once the treatment wears thin and evaporates, the swarm may resettle and remain. You can remedy this by frequently spraying the foliage at least once a week until no traces of infestation are observed.
A baking soda mix would prevent the formation of sooty or black mold fungi since it produces a basic or alkaline surface that reverses the optimal conditions necessary for their growth and proliferation.
Mealy Bugs
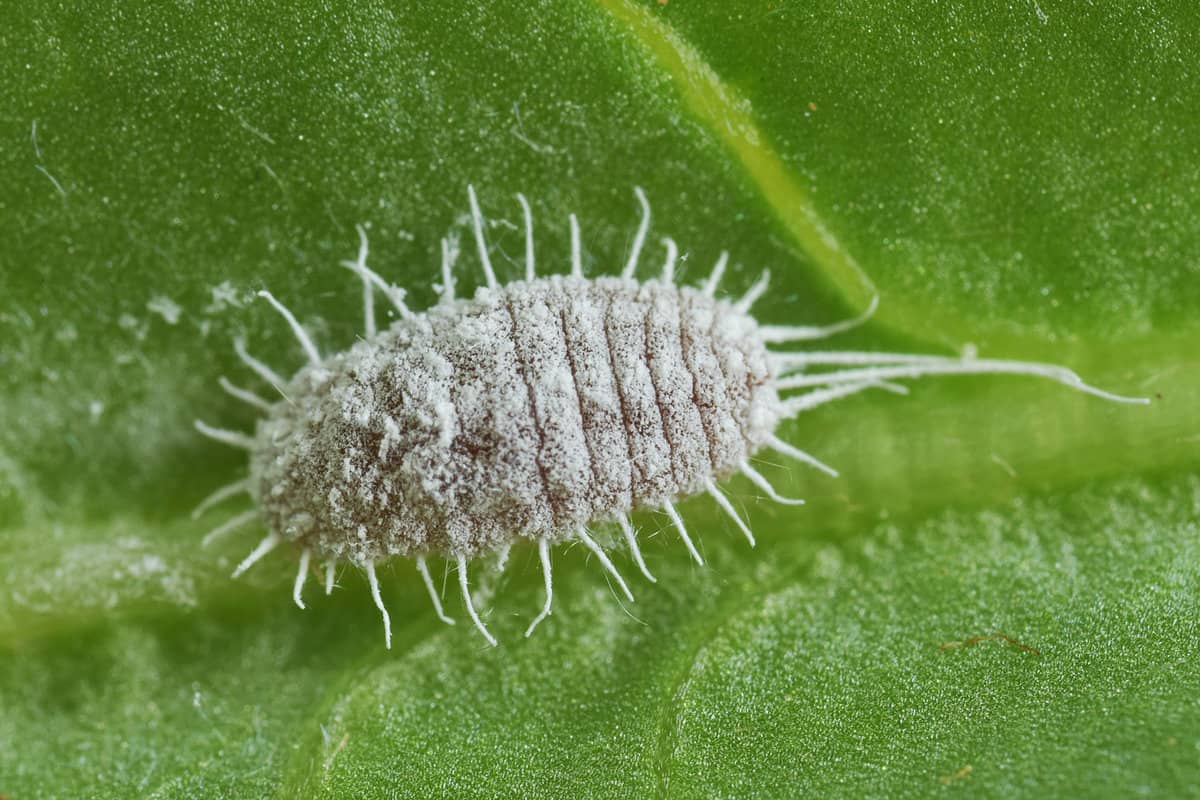

Their waxy coating protects mealy bugs from chemical-based insecticides and renders them resistant to the compound. It is advisable to use natural treatment in constant application to control an infestation.
Grow companion plants that naturally attract mealy bug predators to limit their presence. Lady beetles (mealy bug destroyers), spiders, lacewings, and minute pirate bugs are considered their predators.
You can purchase mealy bug destroyers and release them in your garden or greenhouse during the warmer months. Lady beetles are particularly sensitive to frigid conditions and may not survive if let loose in the winter.
Check out 1500 Live Ladybugs on Amazon.
It is better if the mealy bugs already began laying eggs to support the reproduction diet of the lady beetles.
The use of solutions and horticultural oils helps suppress and control an infestation. Spot treatment entails a lot of work and is mostly used on mildly infested plants. The procedure includes directly dabbing cotton buds dipped in a diluted isopropyl alcohol on the insects.
How To Prevent Pest Infestation?

The best way to prevent mealy bugs, whiteflies, or any infestation is to constantly monitor the plants around your yard, garden, or landscape. Indoor or greenhouse-grown vegetation should be constantly inspected as well.
The key to preventing the onset and spread of disease is to identify early signs and symptoms of plant health deterioration.
Plant pests and diseases commonly spread and infest the rest of your plants from transported and newly-purchased species that may be carriers of unwanted parasites and pathogens.
Check the new acquisitions for any signs of pests and diseases and isolate the plant before introducing or incorporating them into the rest of the landscape.
In Closing
Inasmuch as whiteflies and mealy bugs are similar in terms of traits and mode of action; whiteflies are known to cause more damage to various vegetation since they fly in swarms and transfer from one place to another carrying pathogens and bacteria. We hope the article proved to be helpful!
You might also be interested in these topics:

