Ice plants have specific growth and development needs. So, environmental factors and soil conditions may affect their ability to produce flowers. That said, we researched ice plants to find out how you can care for them properly and promote blooming.
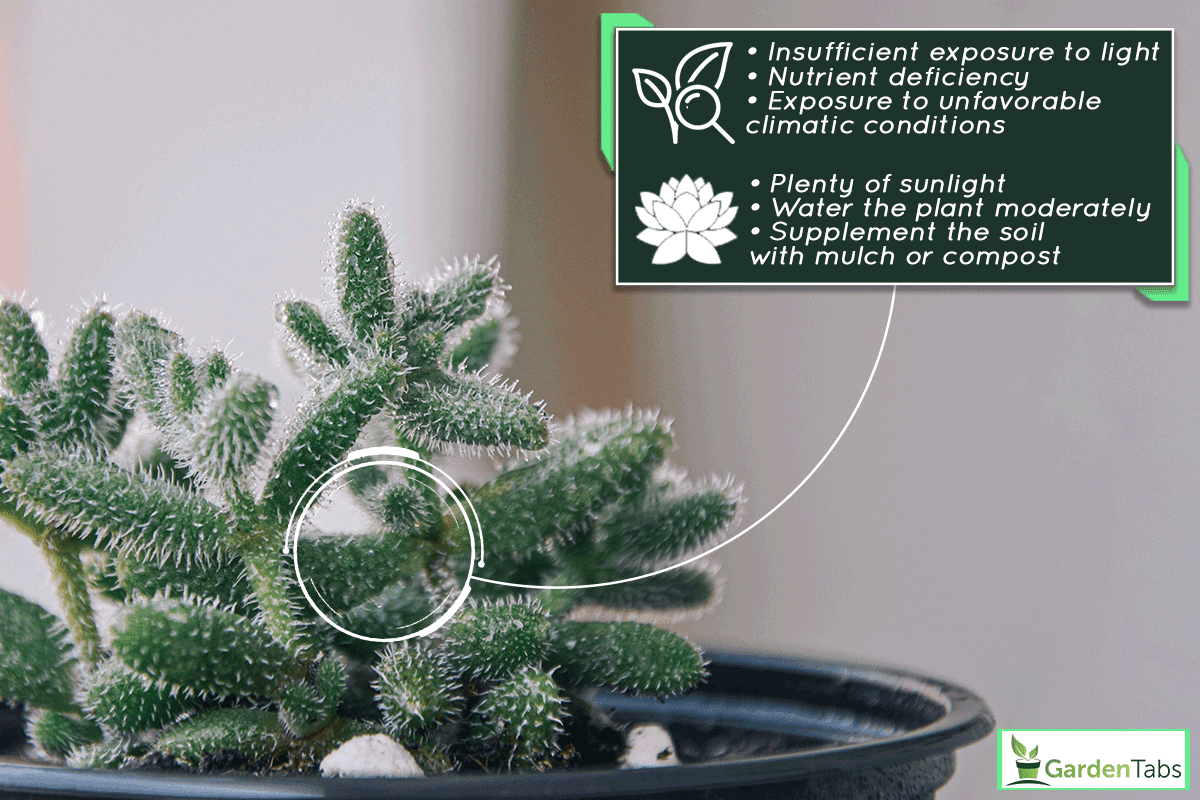
Your Ice plant may fail to bloom due to insufficient exposure to light, nutrient deficiency, and exposure to unfavorable climatic conditions.
The best way to encourage your ice plant to produce flowers is by ensuring it gets plenty of sunlight and applying slow-release fertilizers that promote blooms. In addition, water the plant moderately and supplement the soil with mulch or compost.
Ice plants are relatively easy to grow and propagate when cultivated under the right conditions. However, certain factors may affect the production of blooms and cause the plant to fail. Read on to find out how to encourage the plant to produce flowers!
Common Causes For An Ice Plant That Won't Bloom
These are some reasons why Ice plants may fail to bloom:
Insufficient Exposure To Light
Like most flowering plants, Ice plants do not thrive well in partial shade. They may fail to produce blooms due to inadequate light since they tend to lose their vigor when kept indoors as ornamentals.
Therefore, observe the placement of your plants and note the amount of sunlight it receives during the daytime.
For plants in the yard, garden or landscape, consider the surrounding vegetation like trees or taller shrubs and hedges that may obstruct sunlight. Also, fences or walls may prevent adequate light from reaching the plants.
Nutrient Deficiency
Ice plants require little maintenance when grown on the ground since the naturally occurring soil nutrients are enough to sustain their growth.
Problems tend to occur with potted or container-based plants. Over time, soil fertility becomes poor due to nutrient depletion, and the ice plant may fail to produce blooms.
Unfavorable Climatic Conditions
Temperature, humidity, and the prevailing climate directly influence flower production. Extreme cold can inhibit blooms' development since low temperatures slow down plant metabolism.
Young, developing ice plants are the most susceptible and may even die.
When conditions are too humid, extreme moisture in the air and soil promotes the growth of parasites that cause plants to develop poorly due to stress and lowered resistance.
This affects the plant's ability to produce flowers and foliage.
Pruning
While pruning may increase foliage and branch development, it prevents the formation of blossoms when done prematurely.
Some gardeners choose an inappropriate time to prune their plants aggressively to stimulate plant growth. The best time to prune your ice plant is right after the flowering period since nutrients will be diverted and used to develop new blossoms.
What Are Some Ways To Encourage An Ice Plant To Bloom?
If your ice plant doesn't produce flowers, there are many ways to fix this. We'll discuss them below:
Expose Them To Adequate Light
Ice plants thrive best in full sun; most varieties need at least six hours of exposure. Consider placing plants indoors beside a clear window that allows adequate light to penetrate.
For outdoor planting, position them in clear, unobstructed areas like yards or gardens.
If included in landscapes with trees and other plants, make sure the adjacent growth does not block sunlight and create shade or canopies that may affect the health of your ice plant.
It may be necessary to replant them in well-lit areas if they are developing poorly along the side of the house, near walls or fences obstructing sunlight.
Apply Fertilizer
As mentioned, potted plants tend to deplete soil nutrients over time and may exhibit growth changes like the inability to produce blooms.
Apply organic supplements or fertilizers to remedy the issue and ensure that you choose the right mineral proportion of the additives.
Elements like water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, potassium, and iron, to cite a few, play a role in plant growth. But phosphorus is most responsible for bud, fruit, and flower development.
In addition, phosphorus strengthens the roots and accelerates plant maturity.
Use liquid additives with enough phosphorus content to keep your ice plants flowering. While nitrogen-based applications may stimulate leaf growth, they may fail to contribute to flower development. These additives mainly influence photosynthesis and plant enzyme activity.
Remember that too many additives will lead to fertilizer burn, which is more detrimental to your plant's health.
Water The Ice Plant Moderately

Water and moisture affect a plant's root system the most. Ice plants thrive in dry conditions and are opposed to too much hydration.
Controlled, moderate watering and soil with good drainage will produce well-developed plants that flower regularly.
Overwatering leads to root rot and hinders nutrient absorption. Consequently, your plant experiences poor or diminished health and may eventually die.
Water the plants weekly during hot weather, once every two weeks in a warm climate, and apply mulch in the winter to regulate soil moisture and temperature.
The potting mix for indoor plants should contain approximately equal portions of organic matter to provide nutrient sources and components that promote sufficient drainage, including sand, crushed gravel, or small pebbles.
Deadheading
Deadheading involves the removal of wilted flowers after they bloom to facilitate the propagation of new growth.
Once you prune off the dead structures, the plant utilizes its nutrients to produce blooms that appear after the spent flowers have outlived their lifespan. You may cut off the entire branch to facilitate better growth.
What Are The Different Types Of Ice Plants?
Various species and cultivars are named after the Ice plant.
Lampranthus and Delosperma are the most common varieties. Like ice crystals, the plant consists of tiny hairs that reflect light, hence the name 'Ice plant.'
It is considered a perennial that produces vibrant hues of pink, red, yellow, purple, orange, and bi-colors that thrive well in temperate regions. The leaves are thick, similar to a succulent, and develop a deep green shade during late fall.
Ice plants have a variety of functions, from acting as a ground cover to growing as a bushy shrub, depending on the species. They usually bloom at the start of spring and typically last throughout summer and fall.
Delosperma brunnthaleri
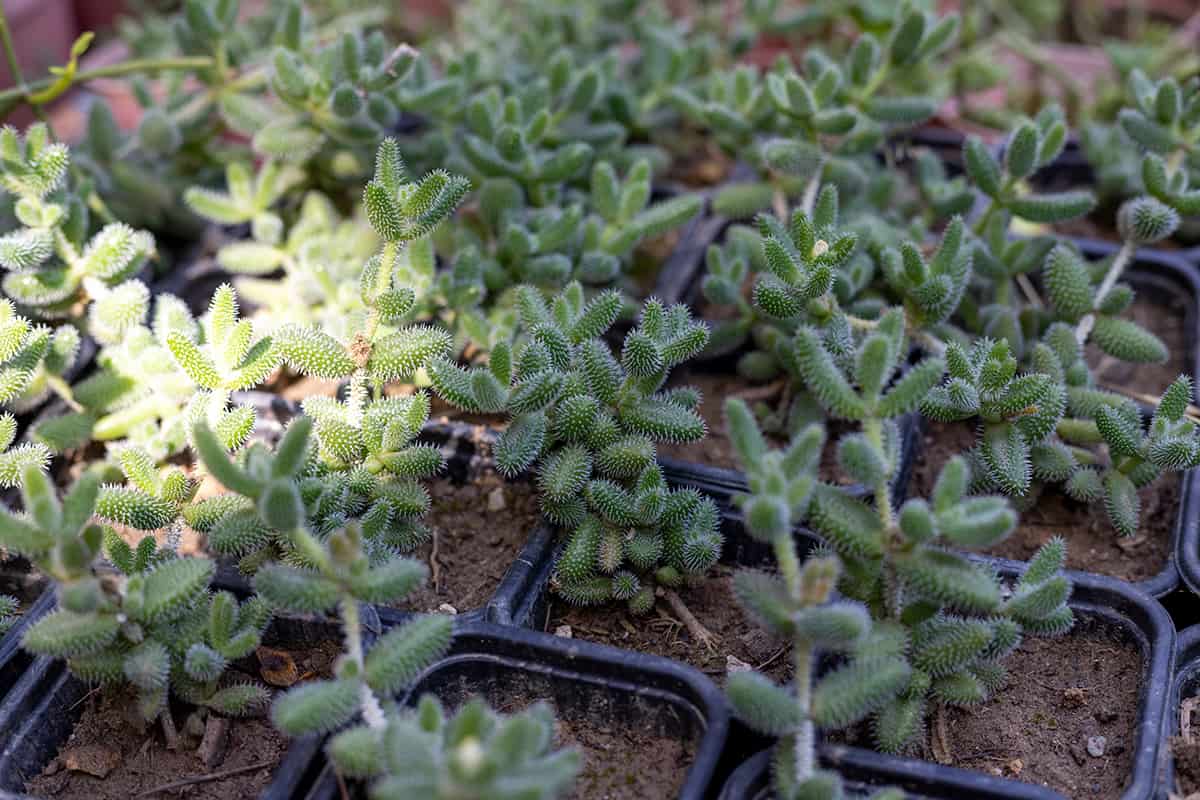

Delosperma brunnthaleri is a small evergreen shrub that grows to a height of 2 inches and produces vibrant pink and yellow flowers. The plant thrives in slightly acidic to neutral soils.
Additionally, it requires full sunlight exposure.
Delosperma floribundum 'Starburst'

Delosperma floribundum, a purple ice plant, is a succulent ground cover that attracts butterflies and other pollinators. It typically blooms throughout the growing seasons.
Starburst prefers sandy well-draining soils, sunny locations, and dry environments. It would be best if you fertilized it often and watered it regularly in its first year.
Once established, the plants require little to no maintenance and only demand hydrating once the soil dries completely.
In various landscaping designs, you can grow the species in containers, flower pots, and baskets and use it as an ornamental plant.
Delosperma cooperi
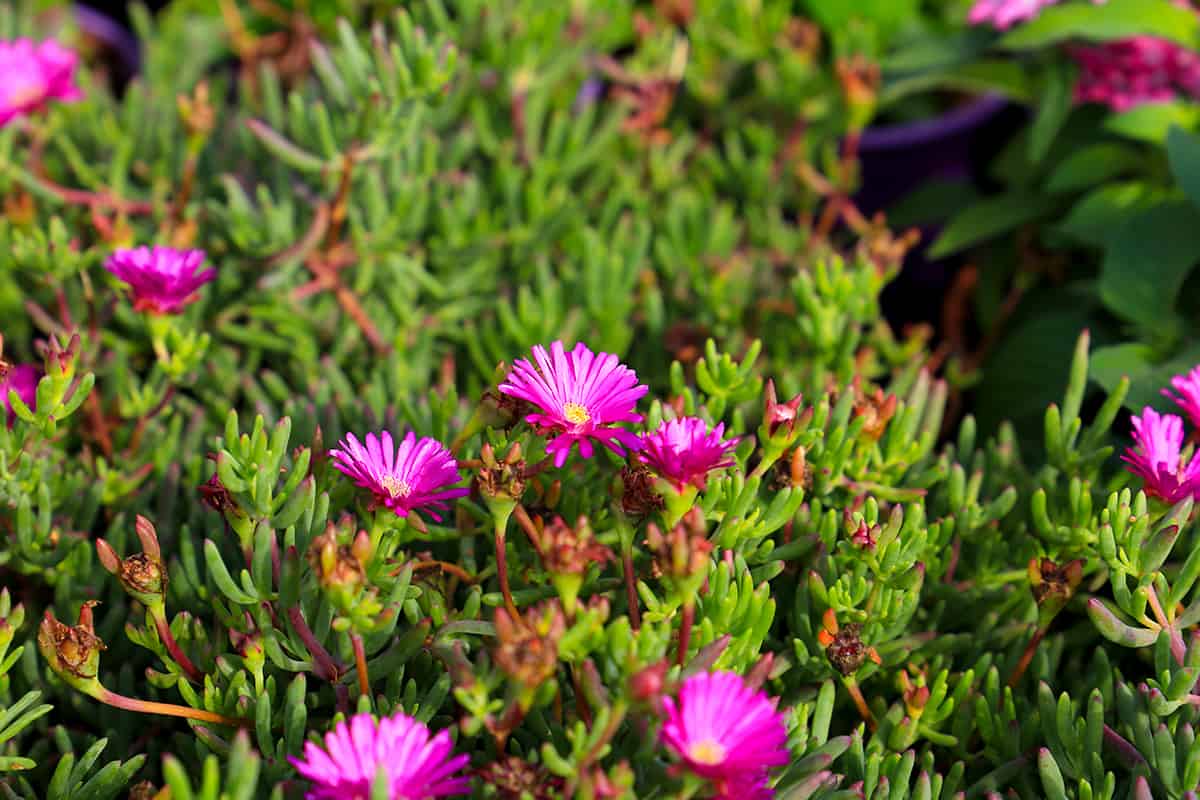

Delosperma cooperi is a hardy ice plant native to South Africa. It is known for its brightly pinkish-purple daisy-like flowers that reach a height of 2 inches.
The plant can grow up to 6 inches (15 centimeters) tall. Because it has lush, light green foliage, it is an excellent ground cover plant.
Since this variety thrives well in dry locations, it is essential to plant it in soils with good drainage. The plant will grow and develop poorly when placed in wet and soggy environments.
The plant repels deer but attracts beneficial insects or pollinators such as butterflies.
Lampranthus aurantiacus
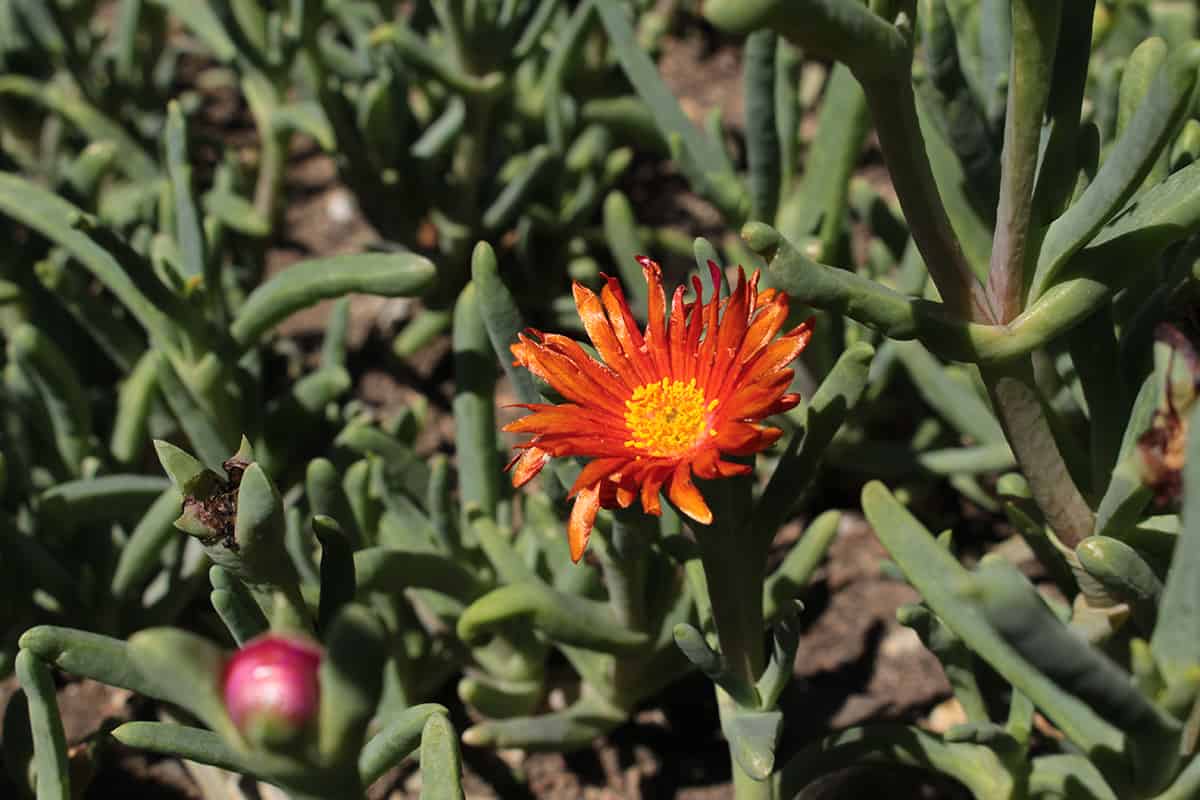

Also known as Orange Ice Plants, this variety develops vibrant orange flowers with yellowish centers. Blooming usually begins in late spring and lasts throughout the summer season.
The succulent reaches a height of 14 inches (35 centimeters) and a spread of 5 feet (1.5 meters).
Lampranthus aurantiacus can survive in any growing condition. However, growing them in sandy or rocky, well-draining soils is ideal.
Mature plants tolerate drought, requiring deep hydrating only amidst long dry spells. On the other hand, newly-planted varieties need to be watered once the first top inch of the soil is dry.
Lampranthus haworthii
Lampranthus haworthii grows as a tall and dense subshrub that reaches a height of 200 millimeters (2 feet). It develops flowers with various shades of white, pink, and pale purple, while the foliage has a bluish-green hue.
Honeybees are generally attracted to their blossoms.
The plant thrives well in well-draining sandy or loamy environments. It is better to hydrate the plant once the soil becomes completely dry because it cannot tolerate moist or damp locations.
To Wrap Up
Ice plants consist of wide varieties. While this is true, their general growth and development needs play a vital role in their ability to produce flowers. We hope this article helped you understand the reasons and provided insightful answers. Happy planting!
Made it to the end? Check out these helpful related posts!
