If you're planning to propagate a plant, one important piece of information to know is whether the plant is a cultivar or not. Knowing this will help you decide whether you can plant it from seed or by using cuttings for grafting. So how can you tell? Here's what our research uncovered about this topic.
To know whether a plant is a cultivar, look for these traits:
- They are hybrids with anatomical differences from the native plant
- They reproduce only through grafting of cuttings, tissue cultures, and controlled seed production
You can also check the plant's scientific name and note these facts:
- The cultivar name is written after the genus or species name of the plant
- The first letter of the cultivar name is always capitalized and the name is not italicized
- The name is enclosed in a single quotation
- It has the abbreviation "cv" before the name which indicates 'cultivated variety'
Read on below as we delve into this topic further. We will give you an example of how scientists write cultivar names, and we'll list down the differences between a plant cultivar and a variety.
How To Identify A Cultivar
If you're preparing for the coming gardening season and browsing seed and plant catalogs, you might encounter the word "cultivar" or "cultivated variety" at some point. It's convenient if the plant already has this label, but what if it doesn't? How can you tell whether a plant is a cultivar or not?

You cannot immediately tell whether a plant is a cultivar or not, especially if you're a novice in horticulture, but here are some ways to figure this out:
1. Look Up The Plant's Scientific Name
The scientific name of the plant can tell you whether the plant is a cultivar or not. According to a horticulturist at the University of Nebraska, here are some things to look for:
- The cultivar name is usually written after the genus or species name of the plant
- The first letter of the cultivar name is always capitalized and the name is not italicized
- The name is enclosed in a single quotation
- It can have the abbreviation "cv" which means 'cultivated variety'
For example, let's look at the Kentucky bluegrass. If its scientific name is Poa Pratensis and the cultivar name is Merion, it would then be written in any of the two ways below:
- Poa Pratensis cv Merion
- Poa Pratensis 'Merion'
Here's a helpful video on how to identify the cultivar name of a plant.
2. Look For Certain Traits
Plants have certain traits that give you an indication that they could be a cultivar. Here are some of them:
- They are hybrids intentionally bred through various cultivation methods
- They have anatomical differences from the mother plant
- They can be reproduced through grafting of cuttings, tissue cultures, and controlled seed production
- Cultivars grown from seeds can have completely different traits from the mother plant
- Cultivars reproduced through grafting has a higher chance of having the same traits as the parent plant
Check out this Live Russian Comfrey Root on Amazon.
What Is Cultivar Identification?
If we're going to be technical about identifying a cultivar, you need to know that you can't accurately tell just by looking at the plant.
Cultivar identification is in fact an entire scientific field of interest and is very important in floriculture and agriculture for plant breeding.
Many cultivars are bred to highlight certain characteristics such as disease resistance, hardiness, and aesthetic appearance. Thus, it is usually intended for fruits, vegetables, and crops to ensure a higher crop yield.
For instance, apples come in around 7,500 different cultivated varieties. Its scientific name is Malus domestica and some of its cultivar names include Abram, Almeda, Ballinora, Beauty of Kent, Cameo, Carlough, Dayton, Delcon, Early Joe, Elektra, Falstaff, Folwell, and many more.
For more in-depth learning, check out this video below on 'Cultivar Identification and Analysis of Seed Purity'.
What Is Different Between Cultivar And Variety?
The term "cultivar" is used by horticulturists and is often interchanged with the term "variety". This is because they can both be written as a part of the scientific name of a plant, usually following the genus or plant species' name.
However, they have major differences in their characteristics, reproduction, and how their scientific name are written.
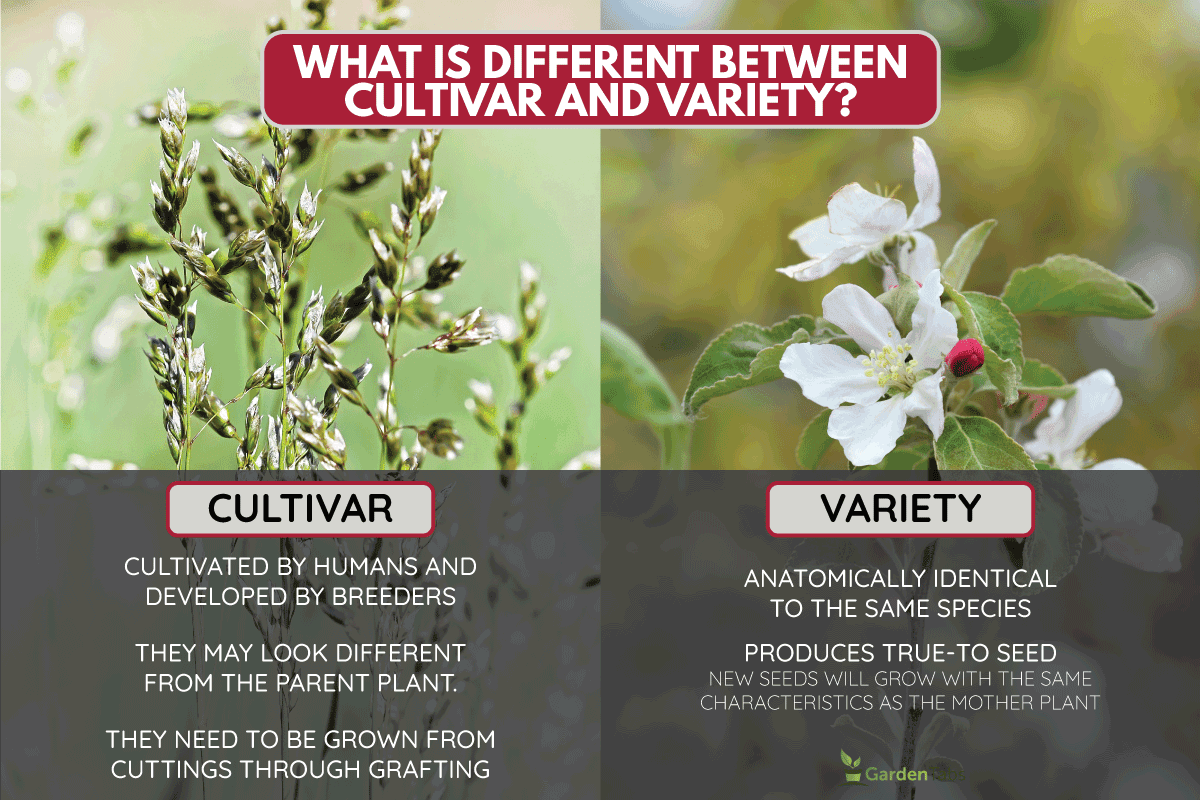
Cultivar
- Cultivated by humans and developed by breeders, which is why they are also called hybrids.
- They are not true-to-seed, meaning if you grow them from seed, they may look different from the parent plant.
- They need to be grown from cuttings through grafting, controlled seed production, or tissue cultures to grow similarly to the parent plant.
Example of how the name of tomato (Solanum lycopercicum) with cultivar name Beefsteak is written:
- Solanum lycopercicum cv Beefsteak
- Solanum lycopercicum 'Beefsteak'
Check out this hybrid large Beefsteak tomatoes on Amazon.
Variety
- Anatomically identical to the same species, except for certain traits such as different color flowers.
- Produces true-to seed, meaning new seeds will grow with the same characteristics as the mother plant.
Example of how the name of an apple (Malus domestica) with the variety name Granny Smith is written:
- Malus domestic var Granny Smith
Here's a great video we found giving a thorough explanation of the difference between a variety and a cultivar.
How Do You Make A Plant Cultivar?
There are four steps to producing a new cultivar:
- Collect germplasm (seeds and tissues for the purpose of plant breeding)
- Specimens are evaluated and planted in a nursery
- Pollination techniques are applied (cross-pollination and self-pollination)
- Cultivars are produced using various techniques including top crossing, mass selection, synthetic variety development, and recurrent selection

What Is The Difference Between A Native Plant And A Cultivar?
A native plant is one that has grown naturally in one particular area. For example, some of the plants and trees native to Florida include the bald cypress, Chickasaw Plum, and the Florida Maple. These particular trees and plants would be hard to find in other places where the temperature and environment are not ideal for their growth.
A cultivar is a plant bred by horticulturists to highlight certain desirable qualities. A cultivar can be bred between two plants (native and non-native) to thrive in a particular area. Most plants are bred to survive extreme cold or hot weather.

What Is The Difference Between Cultivar And Hybrid?
A hybrid is a plant bred between two varieties. This means it gets the characteristics of two different types of plants. They do this usually to gain certain characteristics for higher crop yield and to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
A hybrid is man-made but it can also naturally occur in the wild. If it was made deliberately, it can also be considered a cultivar. Many hybrid plants do not produce seeds, instead, the seeds are produced for commercial use.
Why Is It Important To Develop Cultivars?
There are many controversies surrounding the creation of hybrids and cultivars because many believe that plants should be left alone as nature intended them. However, from another angle, it is seen as a beneficial move to help feed more people through higher yield and ensure certain plants are able to survive.
Creating hybrids helps plants resist diseases, improve their quality, and make them more available and suitable for consumption. It can also help plants tolerate harsh weather conditions and survive longer, even in varying soil conditions.
Companies producing, breeding, and growing plants and seeds are always finding ways to create new cultivars, because according to them, they are more marketable to people. They are always finding ways to have something new to offer.
One last reason why people produce cultivars is out of sheer curiosity. The study of genetic modification of plants allows them to learn more about various plant traits.
Wrapping Up
If you're wondering whether your plant is a cultivar, look up its scientific name or observe how it grows during seasons. Cultivars and hybrids are not true-to-seed and rarely grow from seed. They need to be grafted or grown through tissue cultures and controlled seed production.
Thank you very much for reading through. We hope you were able to learn a few things about cultivar plants and how to propagate them. For further readings on plant propagation, you can read these helpful articles below.
How Do You Prune & Propagate Medinilla? [Step By Step Guide]


