You may wonder if a deciduous tree in your yard is dead when it fails to bud at the normal time. An unhealthy tree can be rescued, but a dead tree threatens your property and safety. We researched deciduous trees to provide accurate information about how you can determine if yours is dead.
One telltale sign of a dead deciduous tree is the absence of foliage or a decline in the number of leaflets. Additional signs are brittle bark that peels off the tree, dead branches, and a mushy or cracking trunk.
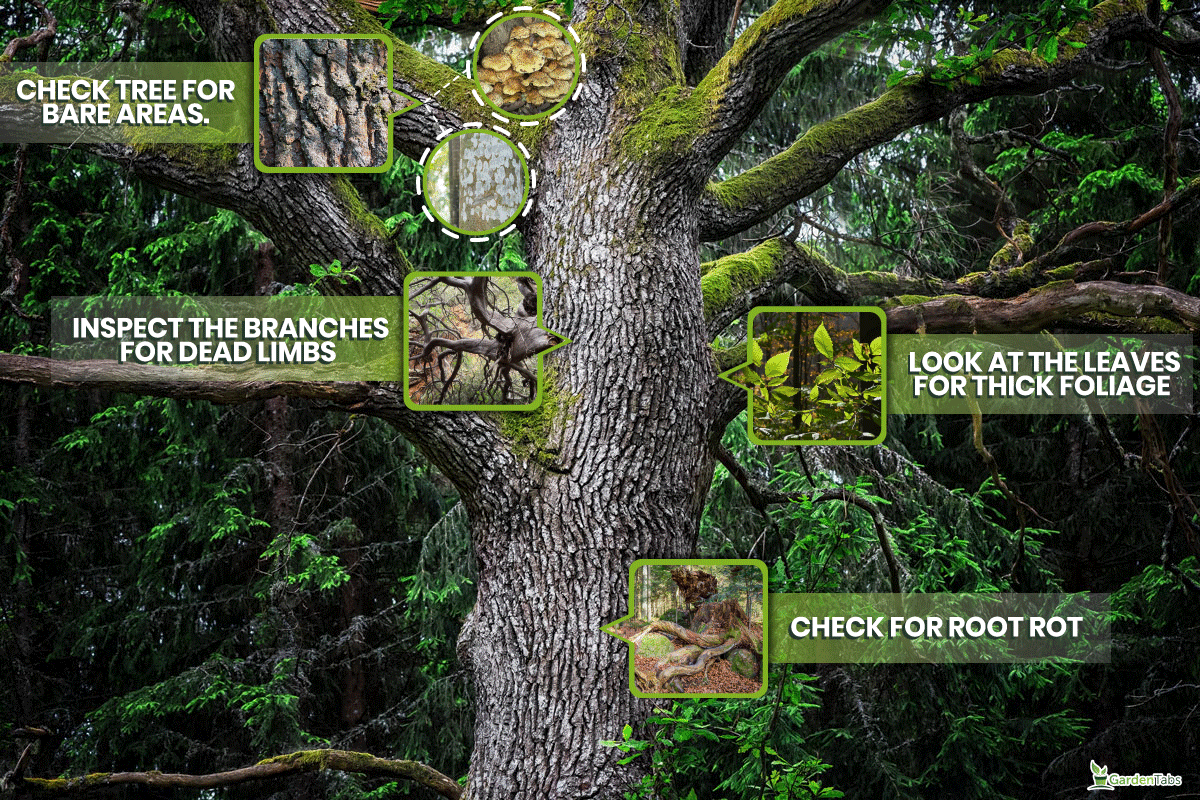
Here is a guide on how to determine if your deciduous tree is dead:
- Check the tree for bare areas, fungal growth, and black and white spots
- Inspect the branches for dead limbs
- Look at the leaves for thick foliage
- Check for root rot
Even though it can be difficult to tell if a deciduous tree is ill, deteriorating, or dead, there are still indicators of vitality to look out for. For more information on how to determine your tree's status, keep reading.
Recognizing A Dead Deciduous Tree
Deciduous trees can be found throughout the United States. They include beech, oak, and maple.
These trees lose their leaves each autumn (the word "deciduous" means "falling off"). Climates that are temperate and moist are ideal for deciduous trees.

A flourishing tree can adapt and survive the toughest environmental circumstances. However, it is possible for them to get sick and die.
The signs of a dying tree are not always evident, so you should learn how to identify them. You might be able to prevent an accident and the need to make costly repairs on your home by recognizing the signs of a dying tree.
Here is a guide on how to determine if a deciduous tree is dead:
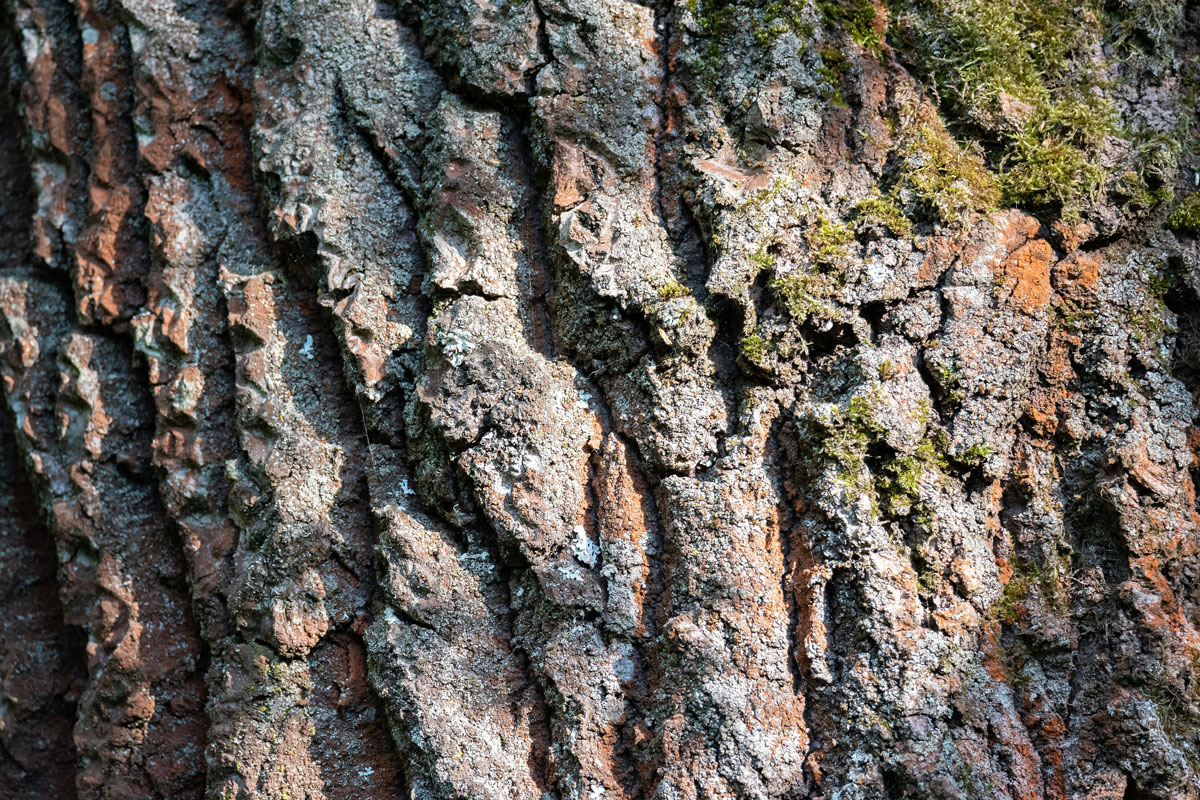
Check The Trunk For Bare Areas

Bare areas or patches where bark is missing on the trunk indicate a problem. In the long run, splitting in tree trunks brought on by the wintertime can be detrimental to the tree and difficult to avoid.
A diseased tree may have extensive splits or cracks that extend deeper than the bark. An additional indication of a dead tree is the presence of carpenter ants. You may see rows of holes left by boring pests.
Examine The Bark For Fungal Growth And Spots

Tree bark alterations constitute one of the most obvious symptoms of tree damage.
The tree needs to be evaluated by an expert if you see fungus or black and white patches on the bark.
A decaying tree's bark can deteriorate and peel off. Insects that consume wood may have formed tree habitats, leaving holes or fungi behind. Bark beetles and brittle bark are both indications of decaying bark.
Use a blade or your fingernails to make little scratches in the bark or branches. A tree that is in jeopardy will have bark that is brown and brittle throughout.
Before deciding if a tree is definitely dead, perform this procedure on several areas of the tree, much like when checking the branches.
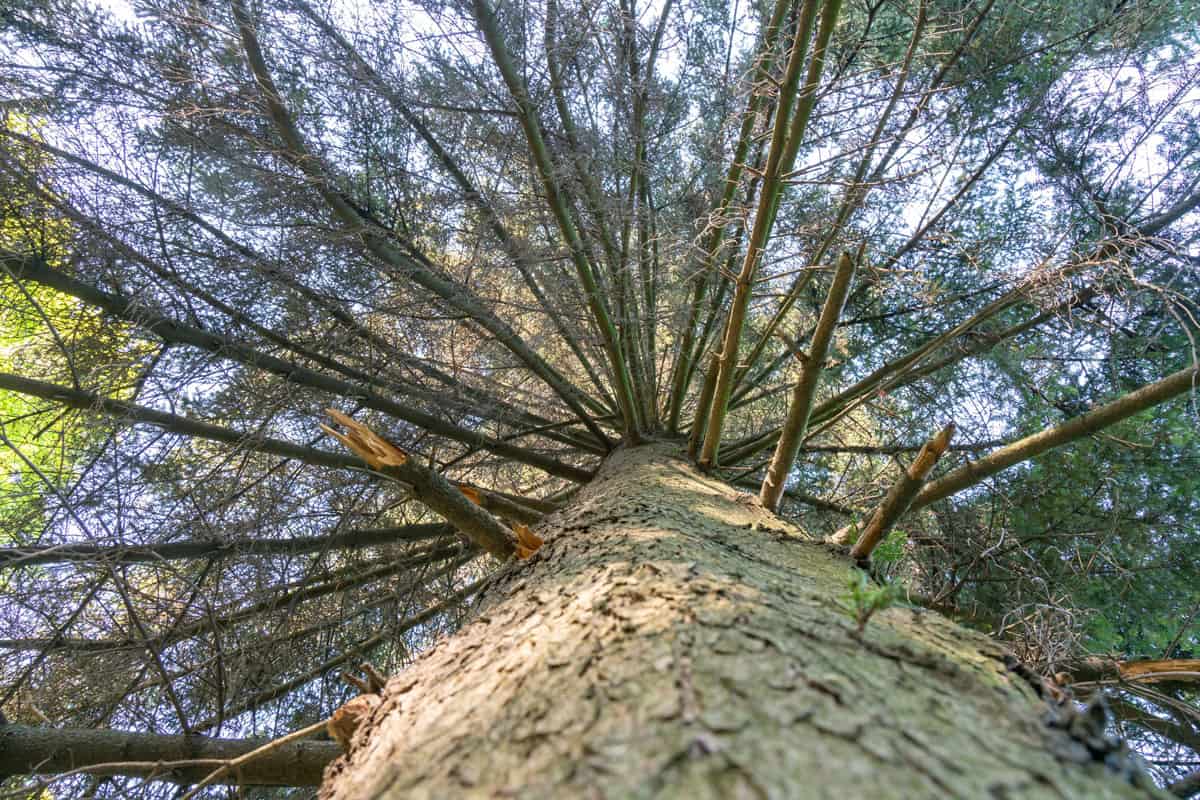
Inspect The Branches For Dead Limbs
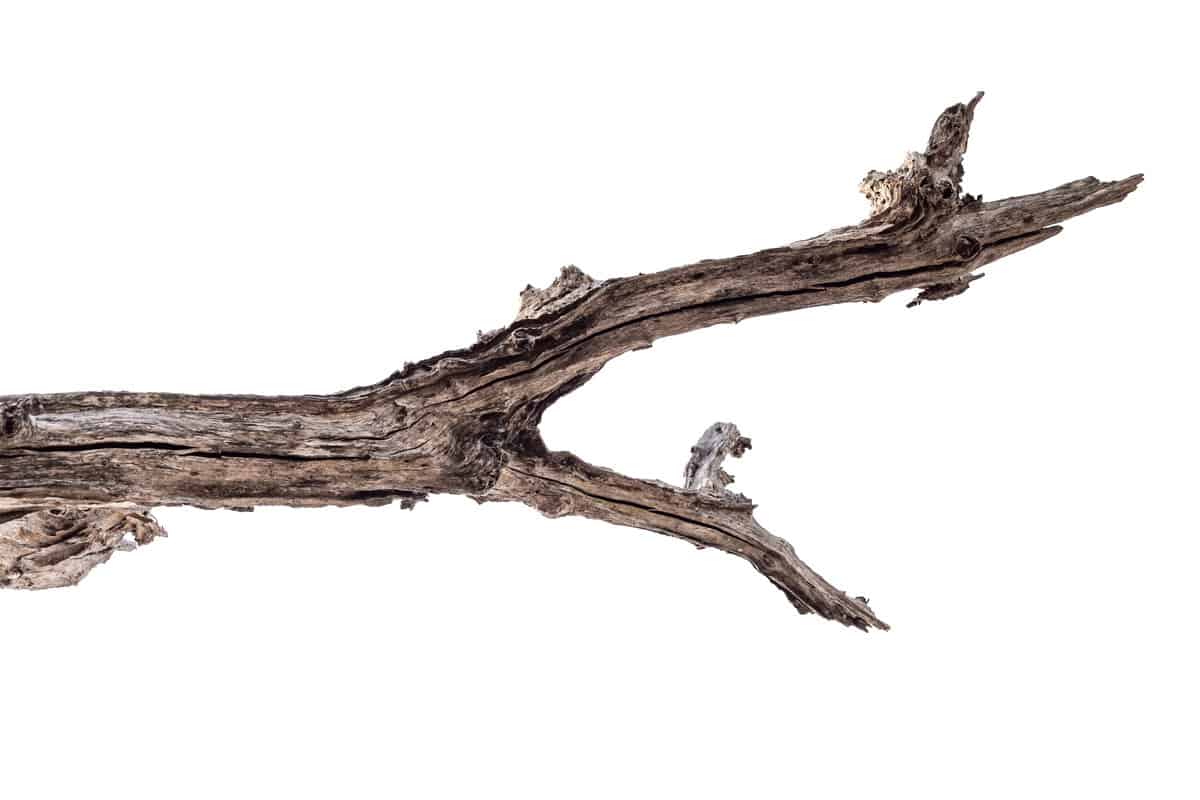

A branch is considered dead when it has completely lost its bark. In extreme situations, diseased limbs will break off. If enough of the branches break off, the tree can die.
It's crucial to remember that a single dead limb or branch doesn't somehow imply that the whole tree is dead. Due to the natural course of a large tree, it will have a few dead branches. But if a tree displays numerous huge, dead limbs, it may have a problem.
One approach to determine whether a branch is healthy is to examine it by twisting a short branch with your forefinger and thumb.
If the branch feels flexible, the tree is probably alive. If it is fragile and cracks, the tree may be dead. You should perform this test in several places, not just with a single branch.
Look At The Leaves For Thick Foliage
Healthy trees have a complete canopy of leaves in the spring and summer. The deciduous tree ought to have some foliage on its limbs unless it is winter.
If a tree is barren in the spring or summer, it could be a sign that the tree is dying. Tree disease may be present if your tree isn't generating any leaves, if its foliage has turned brown, or if the leaves have fallen out in a specific area of the treetop.
When inspecting a deciduous tree's leaves, look closely to determine if some dead leaves are still attached to the tree, whereas the others are naked. The leaf-bearing branches are likely sick or dead.
Normally, trees should lose their leaves. However, if your tree's leaves are stuck or frozen to its branch, the tree may have died recently. There may be several issues if you see stains, sudden changes, or blotches in the foliage.
An ailment may be present if the leaves show a slight discoloration. This might indicate that the tree is not getting sufficient sunshine, water, or essential minerals like nitrogen.
In other words, there isn't sufficient energy to support photosynthesis and the growth of leaves.
Check For Root Rot
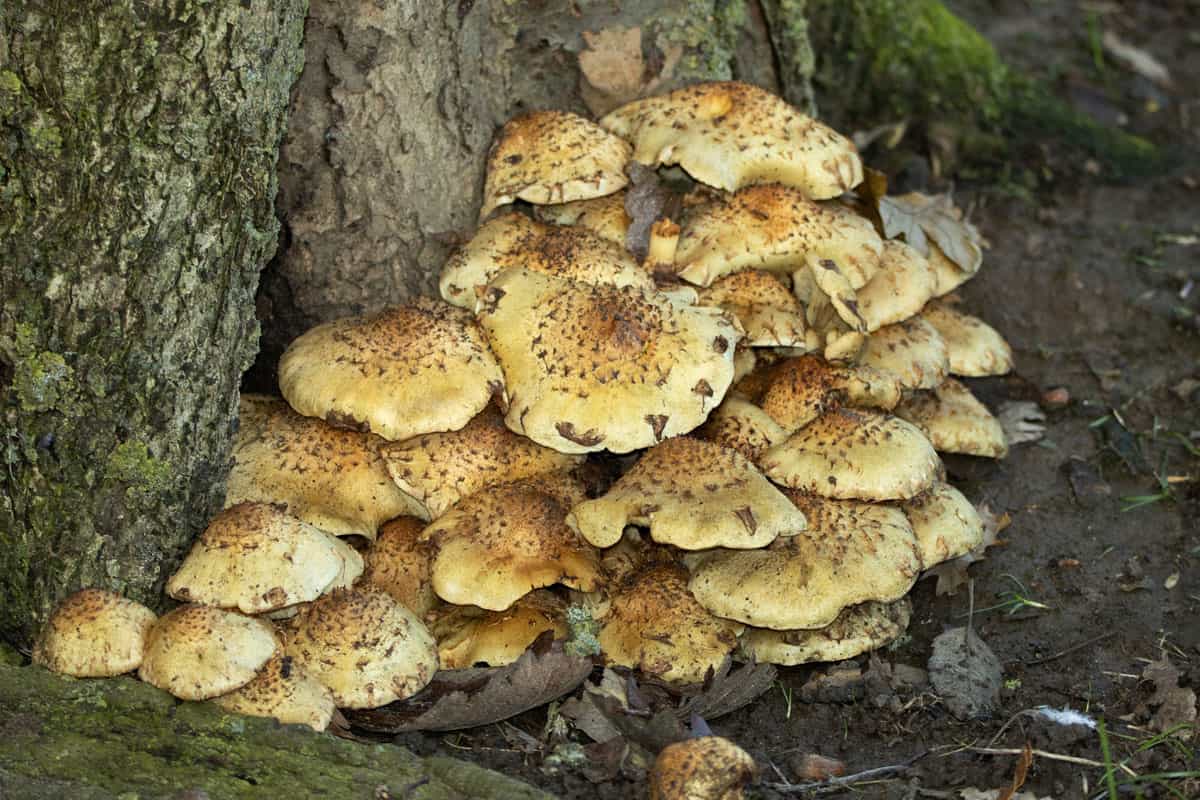

Root rot is another prevalent tree ailment. Healthy roots are crucial since they are necessary for the tree to absorb water, develop, and prosper. In the summer, withered or yellowing leaves signify root rot.
Fungi can spread from one plant or tree that is already diseased to another, or they can infect trees with airborne spores.
A white fluid that appears when the bark is removed and fruiting bodies with a conical or mushroom appearance are indications of a fungus attack.
Engaging a professional to expertly trim your tree and cure the ground to manage the fungus invasion is crucial to prevent the spreading. Additionally, abundant mushrooms near the tree's bottom may be a symptom of serious root rot.
Roots poking up above the surface should also be seen. Roots that are splitting and rising from the ground are the issue here, rather than roots that are sprouting on the surface.
This could mean that the tree is unstable. In either scenario, this can indicate that the tree is in trouble.
Care And Maintenance Of Your Deciduous Tree
Your tree needs regular trimming. Pruning can preserve a plant's wellness and aesthetic appeal, regulate a tree's dimensions, direct growth, or affect fruit or floral production.
Trimming can boost a tree's security by eliminating weakened, sickly, dead, or decaying branches. Choosing appropriate plants for your locality and climate is as crucial as trimming them.
When choosing trees for greenery, you should consider their eventual height and stretch and where the overhead transmission lines are.
The primary goals of trimming trees are to establish and maintain a standard structure and repair hurricane damage and other issues that arise throughout the tree's existence.
Pruning requires the use of the appropriate equipment for the operation. The most skilled pruners will employ numerous tools depending on the dimensions and positioning of the branches they trim.
The same goes for choosing the right tools and for maintaining them. To ensure precise cuts, keep all pruning implements as sharp as possible.
Branch damage from neat trimming is more likely to recover than damage caused by broken tools.
Areas That Need Trimming
- As soon as you become aware of any diseased or dead branches, eliminate them.
- When water shoots and suckers emerge, eliminate them.
- Cut back limbs that are developing inwards or pushing against or obstructing neighboring branches.
- Cut back any stems and branches positioned closely together.
Check out these pruning tools on Amazon.
Pruning Season
Deciduous trees should be pruned when dormant, in late winter or early spring, before bud pause. A tree may become stressed out or produce overwhelming water shoots if significant trimming is performed during the late spring.
You should not trim in late fall or winter because cambial expansion won't be productive to cover the trimming cut. As a result, the bare tissue could die from freezing temperatures.
Check out this pole saw/hedge trimmer on Amazon.
Conclusion

By checking for symptoms such as the absence of foliage or a decrease in the number of leaflets, you can determine if a deciduous tree is dead. Fungi, which feed on dead wood, will also flourish in a dead or dying tree.
Here are some related articles that you may find interesting:
Can I Plant Deciduous Trees In The Fall?


